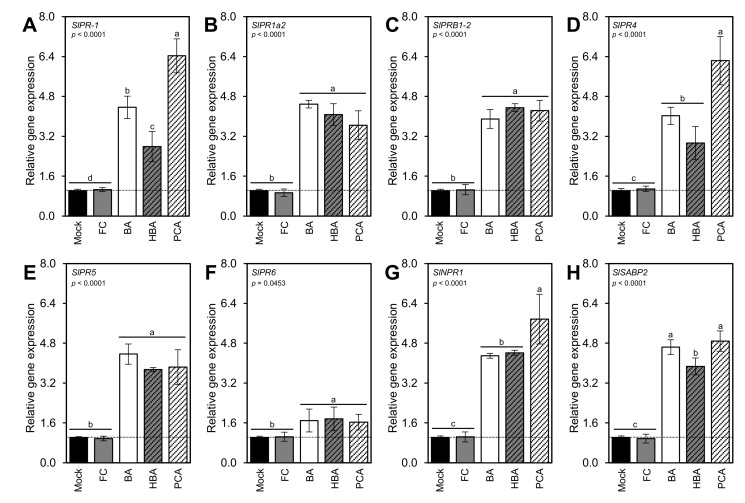
Figure 9.
Benzoic acid (BA) and its hydroxylated derivatives, ρ-hydroxybenzoic acid (HBA) and protocatechuic acid (PCA), induce the expression of pathogenesis-related proteins in A. solani-infected leaves under greenhouse conditions. (A–F) Relative gene expression of six pathogenesis-related proteins (PR) included SlPR-1, SlPR1a2, SlPRB1-2, SlPR4, SlPR5, and SlPR6, respectively. (G) Relative gene expression of nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related protein 1 (SlNPR1). (H) Relative gene expression of the salicylic acid-binding protein (SlSABP2). Values represent the means ± standard deviation (means ± SD) of five biological replicates (n = 5). Different letters indicate statistically significant differences between treatments (p < 0.05). Mock: 0.2% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-treated (mock control), FC: difenoconazole-treated (fungicide), BA: benzoic acid-treated, HBA: ρ-hydroxybenzoic acid-treated, and PCA: protocatechuic acid-treated.