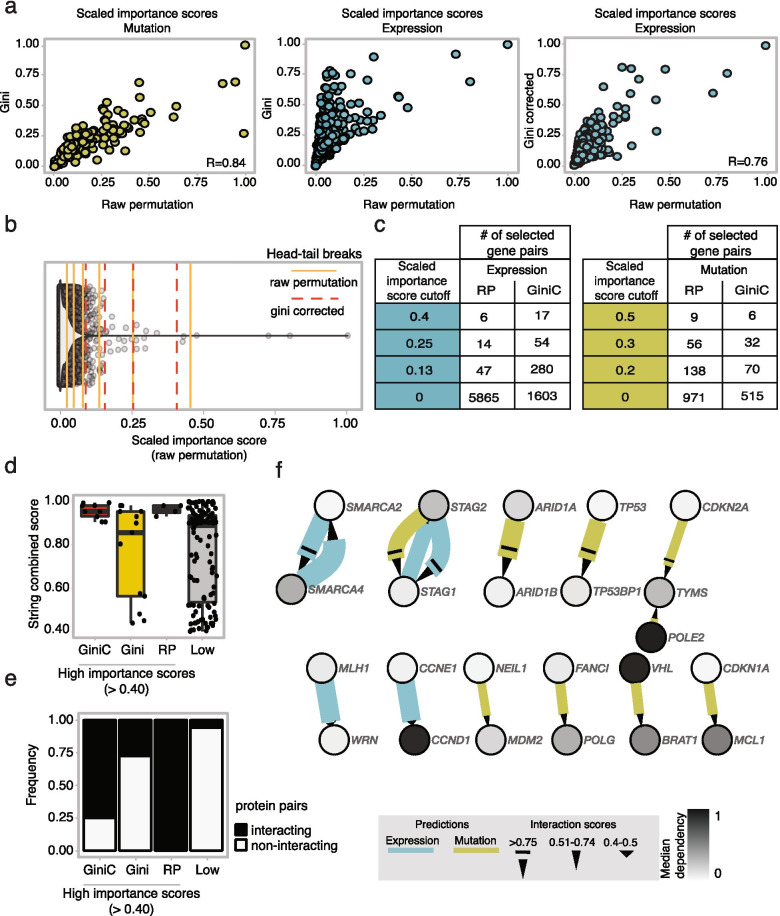
Fig. 2.
Importance score quality assessment and potential synthetic lethal interactions among DDR genes. a Comparisons of importance score calculation methods on commonly selected DDR gene pairs. Gini—raw permutation scaled importance scores correlation using mutation features (green) and Gini/Gini corrected—raw permutation scaled importance scores correlation with expression features (blue). b Density distribution of the raw permutation scaled importance scores with superimposed breaks obtained by the Head/Tail breaks algorithm using raw permutation (yellow lines) and Gini corrected (dotted red lines) importance score methods. c Number of selected gene pairs above different scaled importance score cutoffs based on expression (blue) or mutation (green) features. d STRINGdb combined scores of interacting gene pairs selected with high confidence (scaled importance score > 0.4) by the three approaches and with low confidence (scaled importance score < 0.4) by all of the methods. e Percentage of interacting gene pairs over the selected ones in the four described groups. f Network of predicted SLs among DDR genes based on the raw permutation importance score. Each node represents a gene and each edge a relationship; the arrow starts from the mutated (green) or dysregulated gene (blue) and arrives to the gene showing an associated increased dependency score. The width is proportional to the absolute value of the Pearson correlation coefficient. The color of the node shows the median of the dependency score of the gene in a grey scale. Different arrow shapes show three levels of confidence scores based on the scaled importance scores