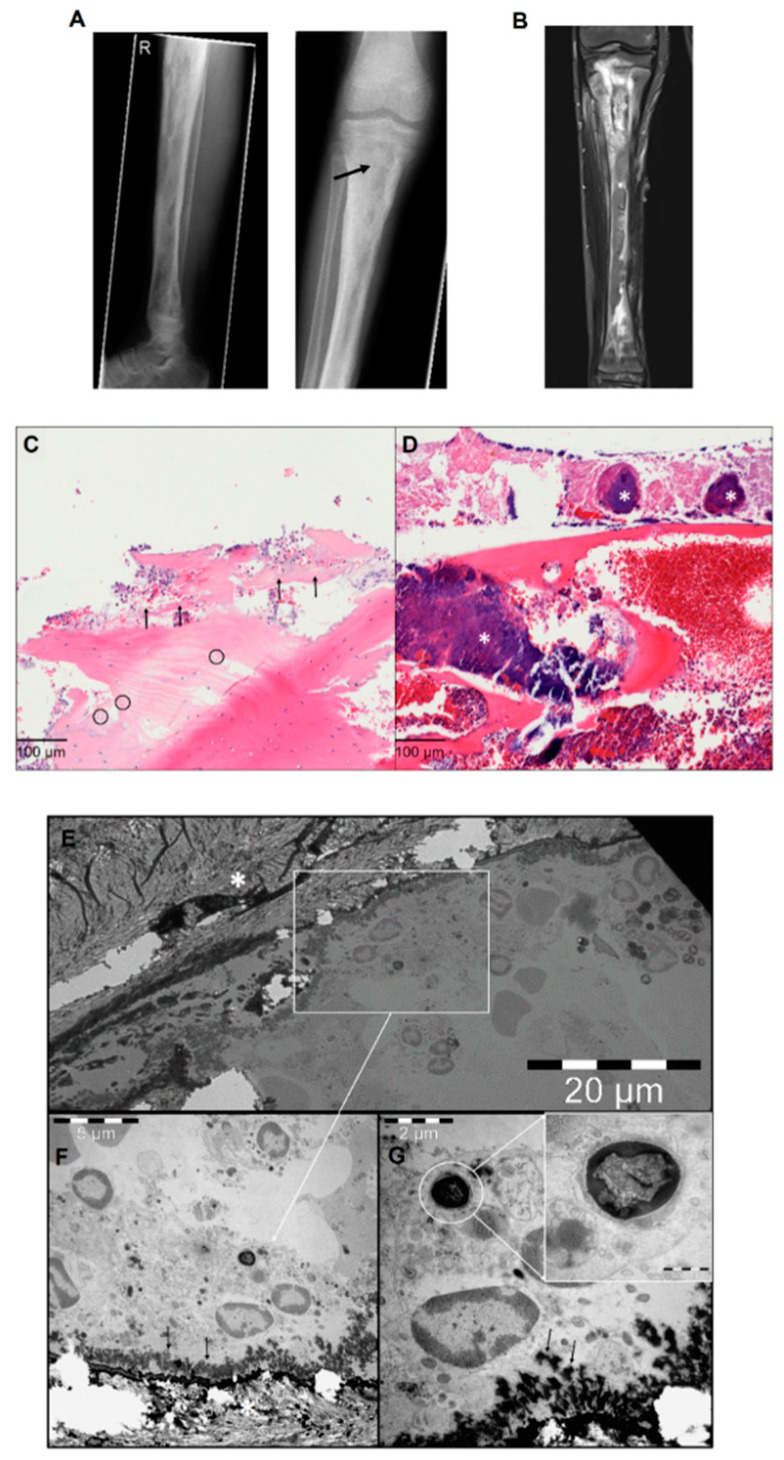
Figure 1.
(A) Preoperative X-rays of the right tibia: periosteal reactions, cortical erosions, focal osteopenia, osteolysis and endosteal scalloping are detectable throughout the long bone. The black arrow in the right panel shows the sampling point. (B) Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging of the right tibia: signs of osteomyelitis are visible. (C) Histological findings of chronic osteomyelitis: bone necrosis with acute inflammatory infiltration (arrow) and empty osteocytic lacunae (circles). (D) Bone necrosis with high amounts of bacterial colonies (*) (HE, ×400). (E) Transmission electron microscope overview images of bone trabecula (marked with the white star) with adjacent osteoblasts. The white square marks the identified region of interest. (F) High magnification of osteoblasts with newly formed osteoid (black arrows) and intracellular Staphylococcus aureus. (G) Osteoblast with magnified intracellular Staphylococcus aureus.