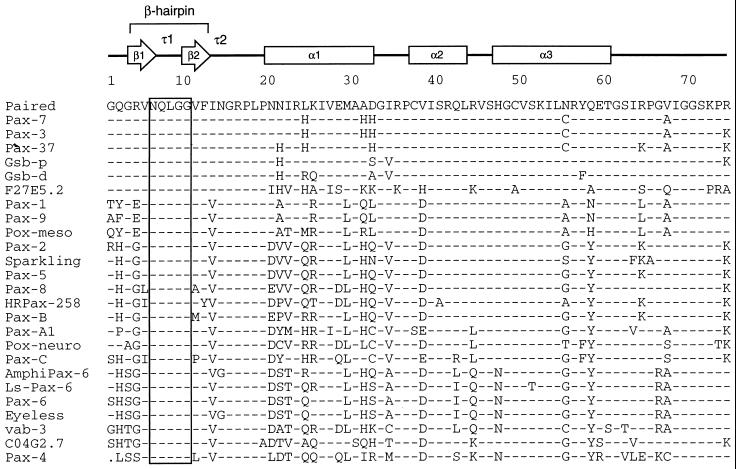
FIG. 6.
The glutamine required for efficient recruitment of Ets proteins (and four flanking amino acids) has been perfectly conserved throughout the evolution of Pax proteins. Amino acid sequences comprising the amino-terminal subdomains and linker regions of Pax proteins were aligned for comparison as shown. Secondary structure of Drosophila Paired is shown with arrows indicating β-strands, boxes indicating α-helical regions, and τ1 and τ2 indicating turns identified in the crystal structure of Paired (53). The β-hairpin is formed by strands β1 and β2 and the type I β-turn τ1, while τ2 is a type II β-turn. Shaded vertical bar indicates the completely conserved region of the β-hairpin, including the glutamine residue analyzed in this report. Sequences were derived from Homo sapiens Pax-1 (EMBL/GenBank accession no. P15863), Pax-3 (P23760), Pax-5 (M96944), Pax-6 (M77844), Pax-7 (Z35141), Pax-8 (L19606), and Pax-9 (S36115); Mus musculus Pax-2 (280984) and Pax-4 (P32115); Branchiostoma floridae (amphioxus) AmphiPax-6 (AJ223440); Halocynthia roretzi (ascidian) Pax-37 (D84254) and HRPax-258 (AB006675); Lineus sanguineus (ribbonworm) Ls-Pax-6 (X95594); Acropora millepora (coral) Pax-C (AF053459); Chrysaora quinquecirrha (sea nettle) Pax-A1 (U96195) and Pax-B (U96197); Drosophila melanogaster Paired (P06601), Gooseberry proximal (Gsb-p; P09083), Gooseberry distal (Gsb-d; P09082), Sparkling (AF010256), Eyeless (X79492), Pox-meso (P23757), and Pox-neuro (P23758); and C. elegans Pax homologs C04G2.7 (Z70718) and F27E5.2 (Z48582) and Pax-6 homolog vab-3 (U31537). The dot in the Pax-4 sequence represents a gap in the alignment.