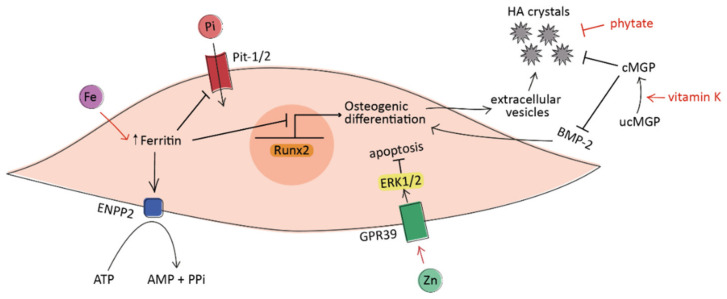
Figure 2.
A simplified schematic representation of the processes under investigation leading to the osteogenic differentiation of VICs in vascular calcification. Iron (Fe) acts at the intracellular level via ferritin, which prevents phosphate uptake and inhibits VICs osteogenic differentiation. Moreover, ferritin promotes the production of anti-calcific pyrophosphate (PPi) from ATP by activating the enzyme ENPP2. Zinc (Zn) induces VICs apoptosis through the activation of the GPR39-ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Vitamin K promotes the carboxylation and activation of matrix Gla protein (MGP), which avoids the formation of hydroxyapatite (HA) crystals and prevents the pro-calcific action of BMP-2. Phytate acts as crystallization inhibitor by binding to HA crystals. The regular arrow denotes “activation”, and the T-shaped arrow stands for “inhibition”.