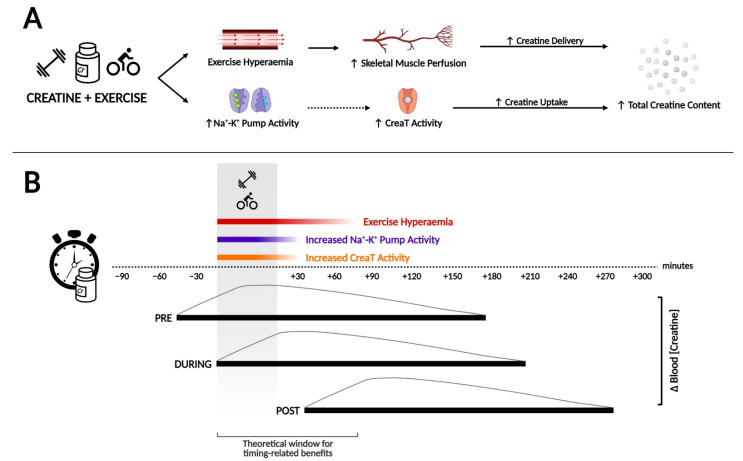
Figure 1.
The hypothetical mechanisms behind an exercise-mediated increase in total creatine content with creatine supplementation. (Panel A): exercise hyperaemia increases tissue perfusion, enhancing creatine delivery. Additionally, increased Na+/K+ pump activity during exercise supports the [Na+] gradient favouring creatine uptake by CreaT. Together, these effects may acutely potentiate the uptake and increase in total muscle creatine content. (Panel B): theoretical overlap of events according to the timing of creatine supplementation, in relation to exercise and its potential benefits regarding the delivery and uptake of creatine to the muscle. Created with BioRender.com.