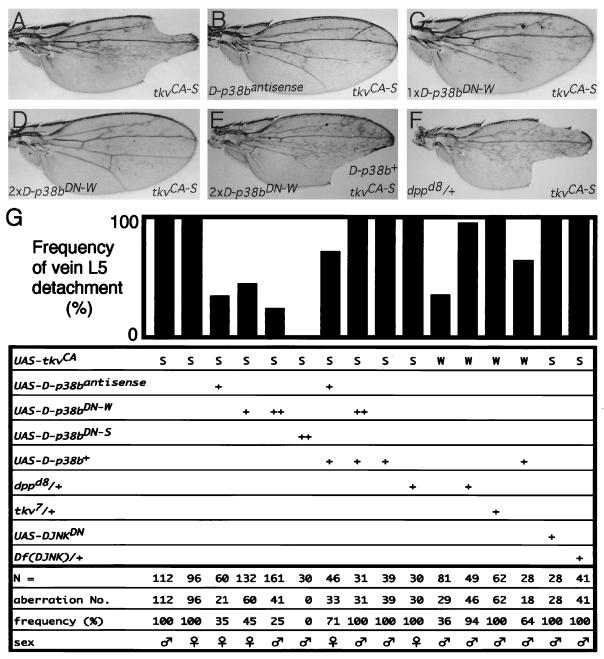
FIG. 5.
Effects of altering D-p38b function and reducing DJNK, Dpp, and Tkv functions on the wing phenotypes caused by either UAS-tkvCA-W (W) or UAS-tkvCA-S (S) driven by 71B-GAL4. (A through F) Adult wing phenotypes. All these wings are from individuals carrying one copy each of UAS-tkvCA-S and 71B-GAL4. (A) Wild-type background for other genes. (B) An individual carrying one copy of UAS–D-p38bantisense. D-p38bantisense suppresses the tkvCA wing phenotype. (C and D) Individuals carrying one copy (C) or two copies (D) of UAS–D-p38bDN-W. D-p38bDN suppresses the tkvCA wing phenotype in a dose-response manner. (E) An individual carrying two copies of UAS–D-p38bDN-W together with one copy of UAS–D-p38b+. Suppression by D-p38bDN was abrogated by coexpression of D-p38b+. (F) Heterozygote of dppd8 (37). Reduction of the dpp gene dosage does not suppress the tkvCA wing phenotype. (G) Quantitative representation. Histograms represent percentages of wings in which L5 is detached from the wing margin. ++, two introduced copies of the transgenes. Df(DJNK), Df(2L)flp147E (46, 50).