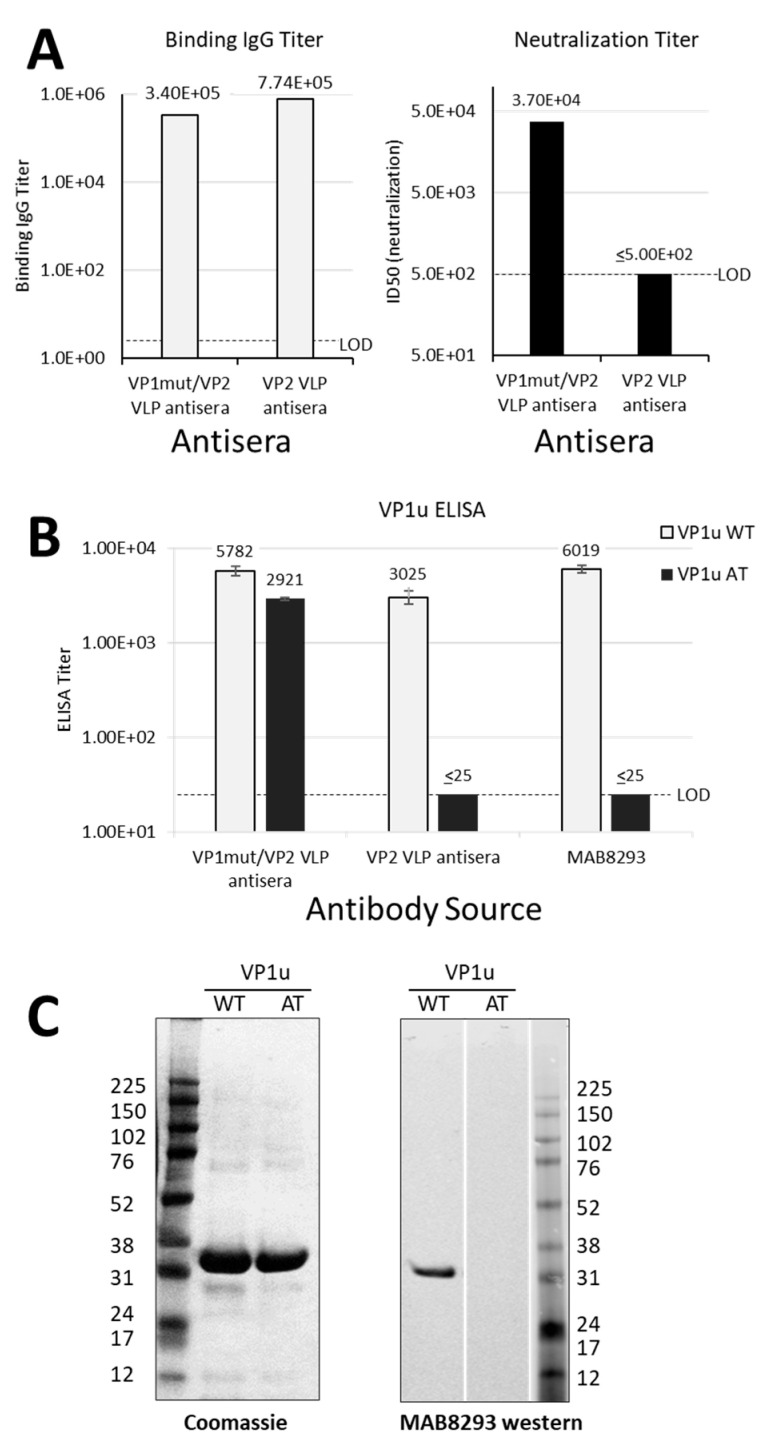
Figure 2.
Differential antibody binding and function. (A) Results in A are graphed from data that were previously reported in table form by Chandramouli et.al. [8]. Pooled sera were from eight mice per group that were immunized either with VP1mut/VP2 VLP or VP2 VLP (see x-axes). These pooled sera were used in an ELISA with plates coated with VP1mut/VP2 VLPs (left). The lower limit of detection for this assay was determined using pre-immune sera (LOD, titer = 5). The same pooled sera were used in a neutralization assay with parvovirus B19 (right). The LOD of the neutralization assay was a titer of 500. (B) The same pooled mouse sera were newly tested in ELISAs with plates coated with peptides VP1uWT or VP1uAT (see legend). The monoclonal antibody mAb8293 was also tested. Means are shown with standard error bars. The LOD of these ELISAs was a titer of 25. (C) Purified VP1uWT and VP1uAT peptides were separated on SDS-PAGE and Coomassie-stained (left). Peptides were also tested by western blot, developed with monoclonal MAB8293 (right).