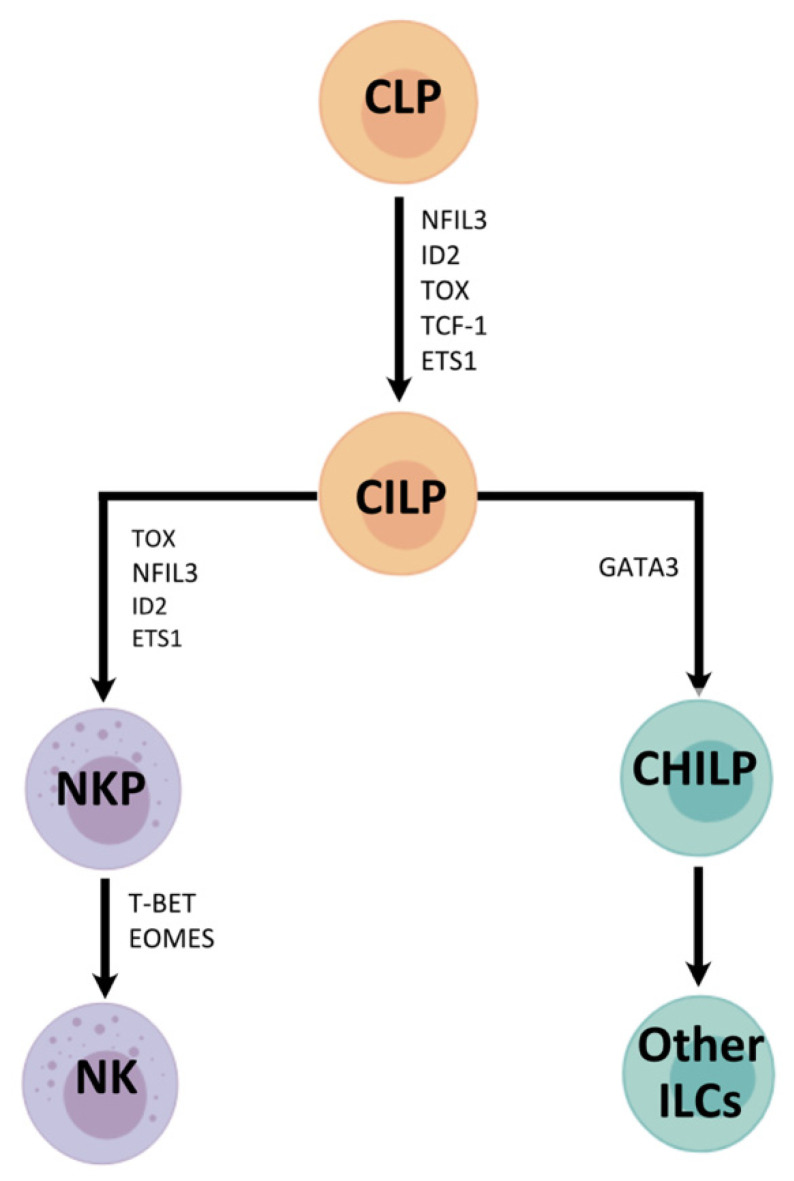
Figure 1.
NK cell development with summaries of the transcription factors required at each stage of differentiation [28]. NK cells originate from common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs), which differentiate into CILPs (common innate lymphoid progenitors). CILPs then differentiate into NK cell precursors (NKP) or common helper innate lymphoid progenitors (CHILPs). The former give rise to NK cells, and the latter develops into other ILCs. NFIL3 = nuclear factor IL-3 induced; ID2 = inhibitor of DNA binding 2; TOX = thymocyte selection-associated high mobility group box protein; TCF-1 = T cell factor 1; ETS1 = avian erythroblastosis virus E26 homolog-1; GATA3 = GATA binding protein 3; T-bet = T-box transcription factor; Eomes = Eomesodermin.