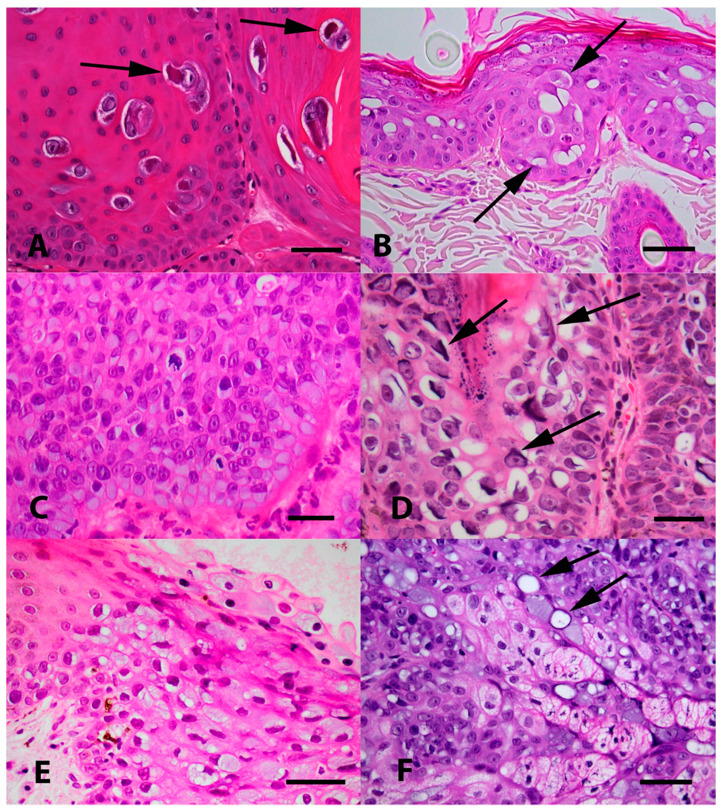
Figure 2.
(A) Photomicrograph of an oral papilloma caused by Felis catus papillomavirus type 1 (FcaPV1). Infection of cells by this papillomavirus (PV) tends to result in the presence of a relatively small proportion of cells developing expanded cytoplasm and nuclei. Within the nuclei, the chromatin becomes compressed peripherally with the presence of a prominent nucleoli. However, the most characteristic feature of FcaPV1 is the development of large prominent eosinophilic cytoplasmic bodies within the expanded cytoplasm (arrows). HE Bar = 30 µm. (B) Photomicrograph of an early Bowenoid in situ carcinoma caused by FcaPV2. Infected cells have expanded cytoplasm that is wispy and blue/grey or clear (arrows). Nuclei are enlarged, but do not have the central chromatin clearing as is visible within cells infected by FcaPV1. Cells within deeper layers of the epidermis have dark shrunken nuclei that are surrounded by a clear halo (koilocytosis). HE Bar = 22 µm. (C) Photomicrograph of a more advanced Bowenoid in situ carcinoma caused by FcaPV2. Many of the cells have expanded cytoplasm that has an amorphous texture and is blue/grey. There is loss of normal epidermal maturation consistent with the diagnosis of intraepithelial carcinoma. HE Bar = 23 µm. (D) Photomicrograph of a Bowenoid in situ carcinoma caused by FcaPV3. Cells in this lesion are expanded, but the cytoplasm is generally clear. Nuclei are enlarged but lack the central clearing. A prominent feature seen in cells infected by FcaPV3 is the presence of large elongated amphophilic to basophilic cytoplasmic bodies (arrows). These are often present adjacent to the nuclear membrane of the cell. HE Bar = 22 µm. (E) Photomicrograph of an area of oral epithelial hyperplasia that contained FcaPV4 DNA sequences. Although additional lesions containing this PV type are required to make definitive conclusions, infection has resulted in increased blue-grey slightly granular cytoplasm. Nuclei do not appear to be markedly enlarged and are typically displaced to the periphery of the cell. HE Bar = 25 µm. (F) Photomicrograph of a Bowenoid in situ carcinoma associated with FcaPV5. The cells that were infected in this lesion were close to the base of the hair follicle and within sebaceous glands. While additional cases are required, the presence of sebaceous glands that have blue-grey expanded cytoplasm should be considered suggestive of infection by this PV type. Another feature visible is the presence of cells that have a single large cytoplasmic vacuole that has compressed the remainder of the cytoplasm to the periphery (arrows). HE Bar = 35 µm.