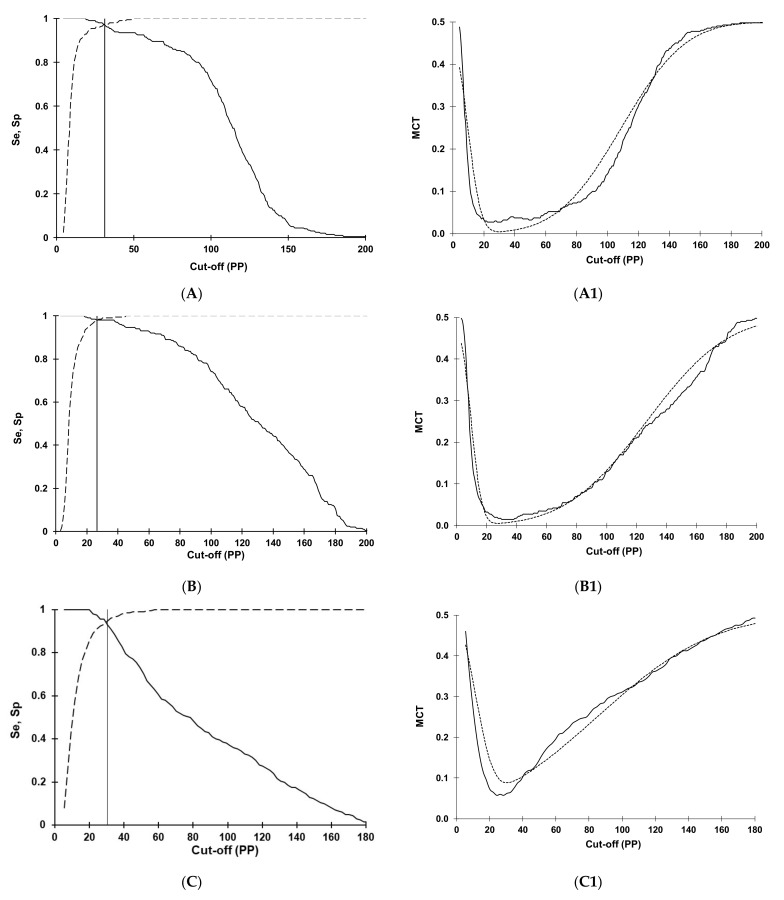
Figure 1.
Optimization of cut-offs for the Rift Valley fever IgG indirect ELISA based on recombinant nucleocapsid antigen in sheep (A), goats (B), and cattle (C) using the two-graph receiver operating characteristic analysis (TG-ROC). The insertion point of the sensitivity (Se, smooth line) and specificity (Sp, dashed line) graphs represents a cut-off PP value (31.23, 26.57, and 30.46, respectively) at which the highest and equivalent test parameters (Se = Sp) are achieved at 95% accuracy level. Using the misclassification cost term (MCT) option of the TG-ROC, at these cut-off values, the overall misclassification costs in sheep (A1), goats (B1), and cattle (C1) become minimal (0.0045, 0.0054, and 0.0625, respectively) under the assumption of 50% disease prevalence and equal costs of false-positive and false-negative results. The two MCT curves represent values based on non-parametric (smooth line) or parametric (dashed line) estimates of Se and Sp derived from datasets in field-collected sera.