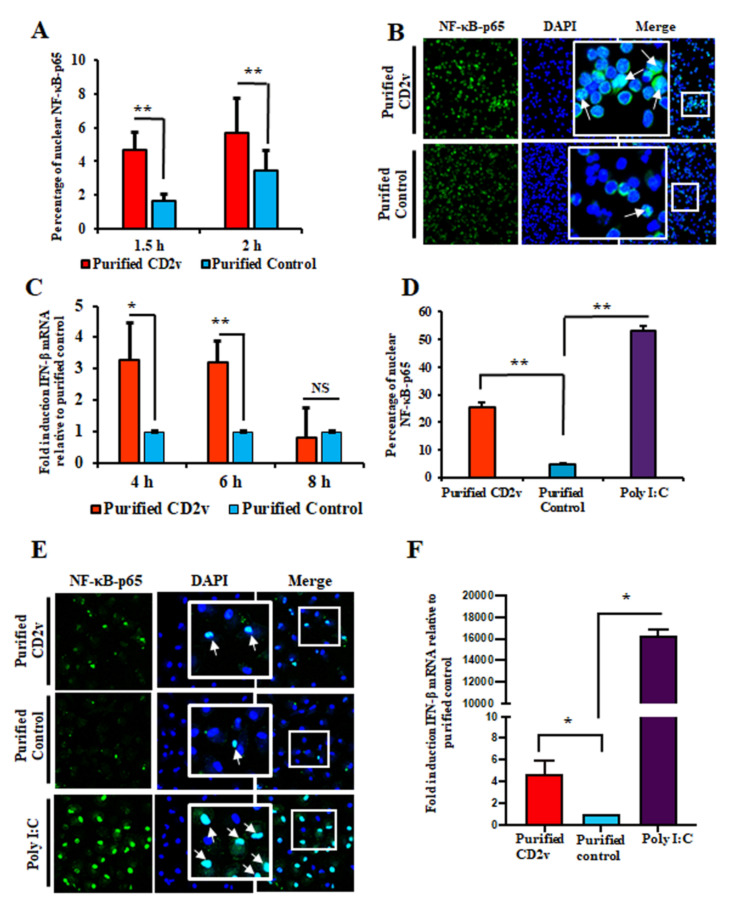
Figure 6.
Purified CD2v protein induces NF-kB-p65 nuclear translocation and IFN-β transcription in swine PBMCs and macrophages. (A) NF-kB-p65 nuclear translocation in swine PBMCs. Swine PBMCs were treated with purified CD2v or purified control, fixed at 1.5 h and 2 h post treatment and assessed for NF-κB-p65 nuclear translocation by immunofluorescence as described in Materials and Methods. Approximately 2000 cells were counted/slide and results are shown as mean values from four independent experiments (1.5 h, p = 0.01; 2 h, p = 0.01). (B) Representative confocal images of NF-κB-p65 nuclear translocation. Green, NF-κB-p65; Blue, DAPI. Insets show magnified areas of the field. Arrows indicate nuclear NF-κB-p65. (C) IFN-β transcription. Cells were treated as in A, total RNA harvested at 4 h, 6 h and 8 h post treatment and IFN-β transcription assessed by RT-PCR. Fold changes are relative to purified control and data are the mean mRNA levels of seven independent experiments (4 h, p = 0.016; 6 h, p = 0.002). (D) NF-κB-p65 nuclear translocation in macrophages. Primary swine macrophages were treated with purified CD2v or purified control, fixed at 2 h post treatment and assessed for NF-κB-p65 nuclear translocation as in A. Approximately 300 cells were counted/slide and results are shown as the mean values from three independent experiments (for purified CD2v, p = 0.002). (E) Representative images of NF-κB-p65 nuclear translocation in macrophages. Green, NF-κB-p65; Blue, DAPI. Insets show magnified areas of the field. Arrows indicate nuclear NF-κB-p65. (F) CD2v-mediated induction of IFN-β in swine macrophages. Primary swine macrophages were treated with purified CD2v or purified control, the total RNA was harvested at 6 h post treatment and IFN-β transcription was assessed by RT-PCR. Fold changes are relative to the purified control and data are the mean mRNA levels of three independent experiments (for purified CD2v, p = 0.034). (*, p < 0.05 and **, p < 0.01).