Figure 4. Methylated ligands partition into and compete for tudor domain binding sites.
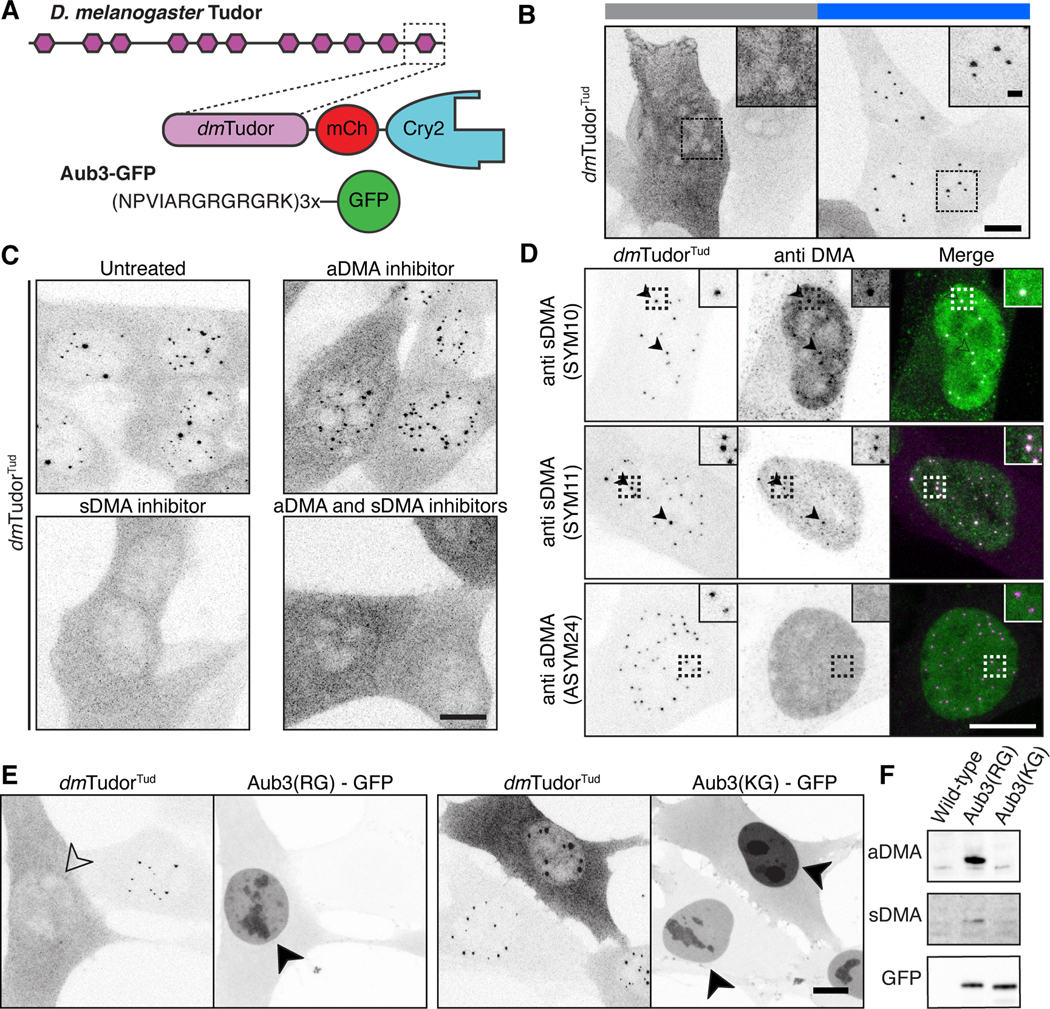
A) Schematic of D. melanogaster Tudor, dmTudorTud and its ligand Aub3-GFP (Liu et al., 2010). B) Fixed NIH-3T3 cells expressing only dmTudorTud in Cry2-inactive and Cry2-active states, revealing condensation property of dmTudorTud. C) Fixed cells expressing dmTudorTud, either untreated, treated with MS-023, EPZ015666, or both inhibitors. D) dmTudorTud counterstained for sDMA (SYM10 & SYM11) or aDMA (ASYM24). Arrowheads indicate colocalized condensate and counterstain. Dotted line insets are enlarged twofold. E) Fixed cells expressing dmTudorTud and either Aub3-GFP or the non-binding, control peptide with R to K mutations (KG). Condensates are inhibited by expression of intact Aub3-GFP (open arrowhead); both Aub3-GFP proteins concentrate in the nuclei (filled arrowheads) of transfected cells that lack condensates. F) Western blot of whole cell lysates of cells expressing Aub3(RG)-GFP, or Aub3(KG)-GFP. Each panel shows the range of ~25–40 kDa. Cry2 is active except where noted in panel B. Scale bars = 10 μm, inset scale bars = 2 μm.
