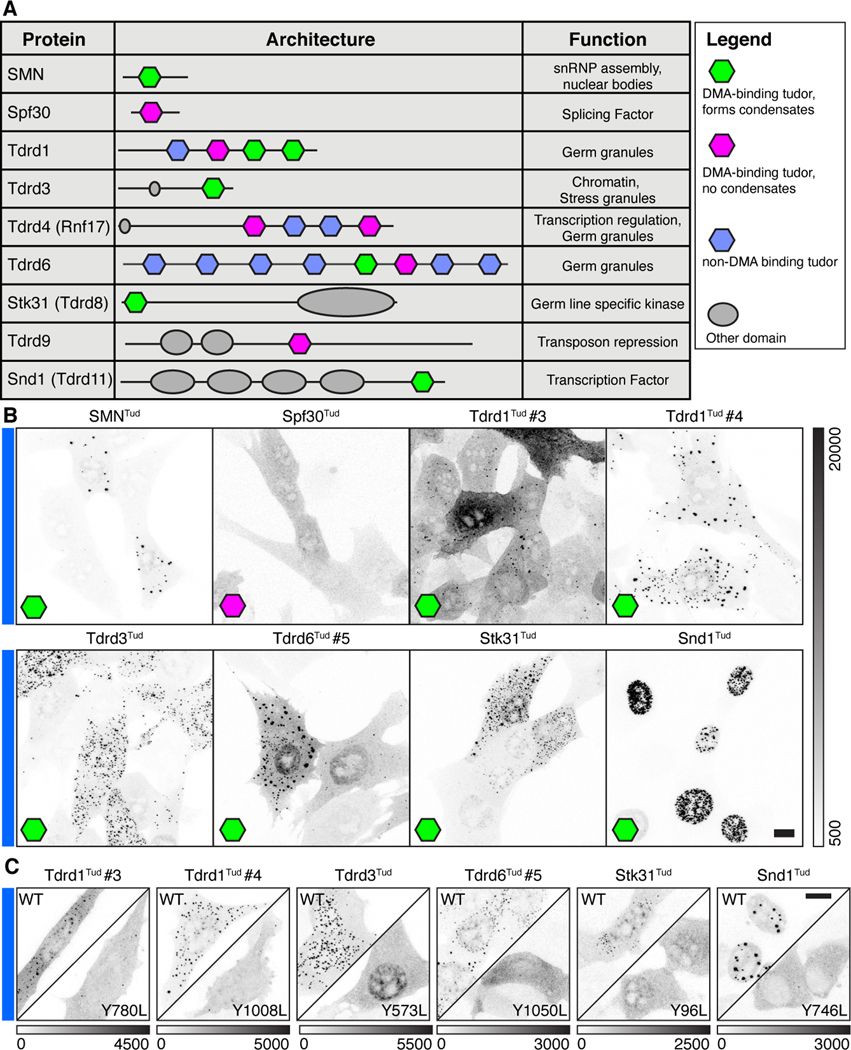
Figure 5. Condensation is a shared property of multiple human tudor domains.
(A) Table of proteins and schematics of human tudor domain proteins tested for condensation,with tudor domains containing either an intact binding site for DMA that form condensates (green), DMA binding tudor domains that do not form condensates (pink), or tudor domains lacking the DMA binding pocket (blue). Domain architecture and function correspond to Uniprot annotations. B) Fixed NIH-3T3 cells expressing Tudor-Cry2 constructs under Cry2-active conditions, corresponding to eight of the tudor domains above (see Figure S6 for more details). C) Fixed NIH-3T3 cells expressing Tudor-Cry2 constructs under Cry2-active conditions where the designated tudor domain is either wild-type (WT) or mutated as indicated to disable the aromatic DMA-binding cage. Grayscale bars given in analog-digital units. Scale bars = 10 μm.