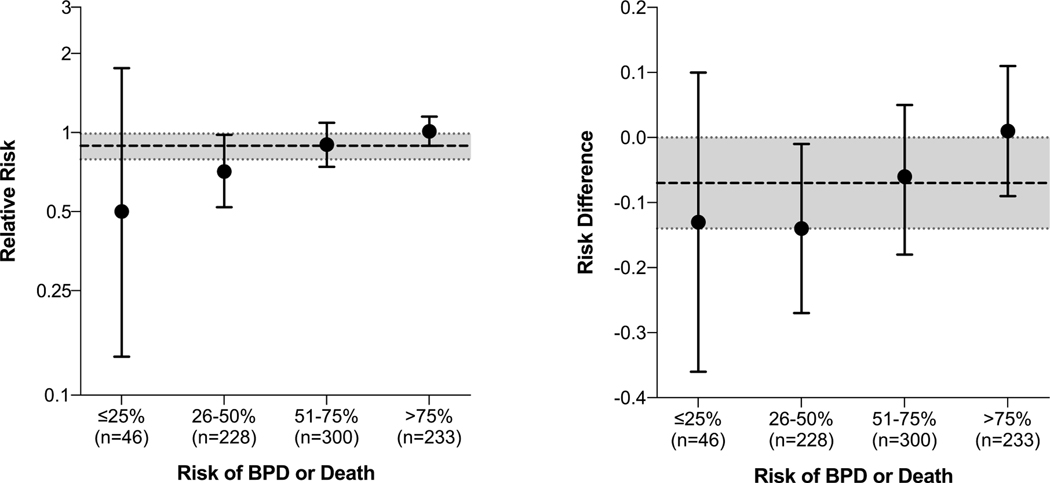
Figure 5.
Observed effect of vitamin A therapy by risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia or death subgroup
Circles and bars represent point estimates and 95% confidence intervals, respectively. Categories shown are defined by 25% increments of risk (rather than quartiles, as shown elsewhere in the manuscript, including Table 2). The dashed and dotted lines represent the overall estimates of effect across all risk groups, as reported in the primary report of the trial. A formal test of interaction, using risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) or death as a continuous variable (not categorized, as shown here), showed that the effect of vitamin A therapy depended upon infants’ risk of BPD or death (p=0.03 for interaction on the relative risk scale; p=0.04 for interaction on the risk difference scale).