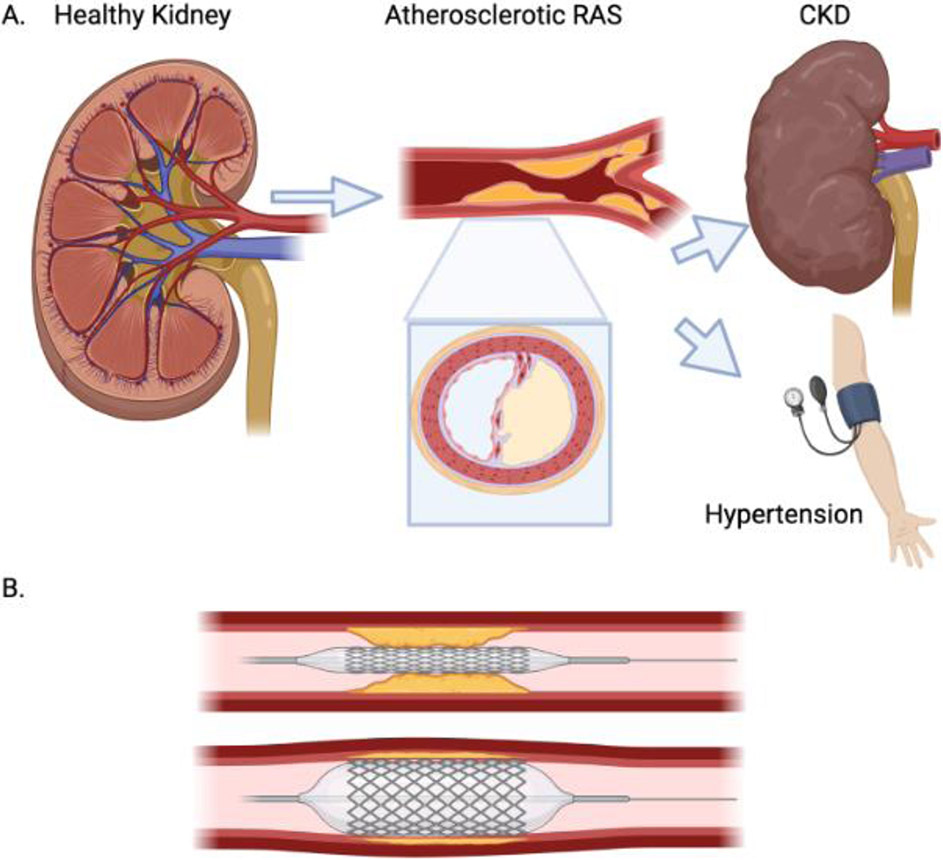
Figure 2. Development and revascularization of renal artery stenosis (RAS).
A. Development of atherosclerotic (or other) lesions in the renal artery (seen in longitudinal and cross-sections) may lead to development of hypertension and to chronic kidney disease (CKD). B. During percutaneous transluminal renal angioplasty (PTRA), a balloon (often with a stent mounted on it) (top) is inflated in the stenotic renal artery (bottom) to dilate the obstruction. The balloon is subsequently deflated and disengaged, leaving the stent engrafted in the renal artery to keep it open. Created with BioRender.com.