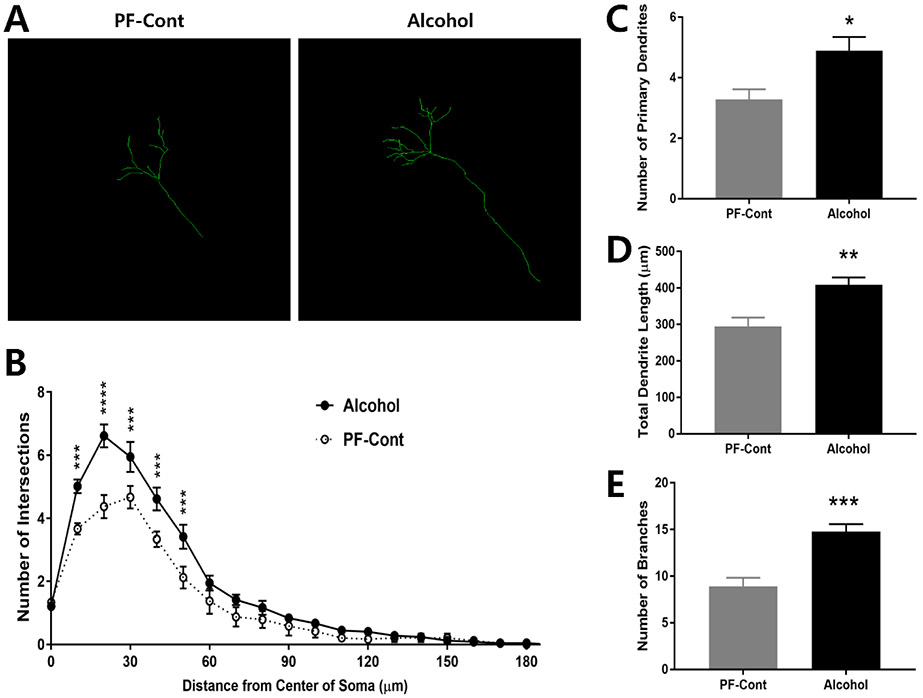
Figure 1. Prenatal exposure to alcohol results in increased dendritic length and complexity in hippocampal CA1 neurons of postnatal day 10 (PND) offspring.
(A) Representative Z-stack confocal images illustrate dendritic branches of CA1 pyramidal neurons from PND 10 offspring following prenatal alcohol exposure (Alcohol) and their pair-fed controls (PF-Cont). (B) A 3-dimentional Sholl analysis revealed significantly more intersections of the dendritic processes at 10-50 μm from the center of soma of CA1 neurons in Alcohol rat, compared to their PF-Cont. (C) CA1 neurons from Alcohol rat exhibited increased number of the primary dendrites compared to PF-Cont. (D) The total dendrite length, and (E) the number of branches were significantly increased in the CA1 field of Alcohol compared to those in PF-Cont. Significance was established a priori at P<0.05; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. n=6 animals derived from 6 litters; 4 neurons/animal.