Fig. 1.
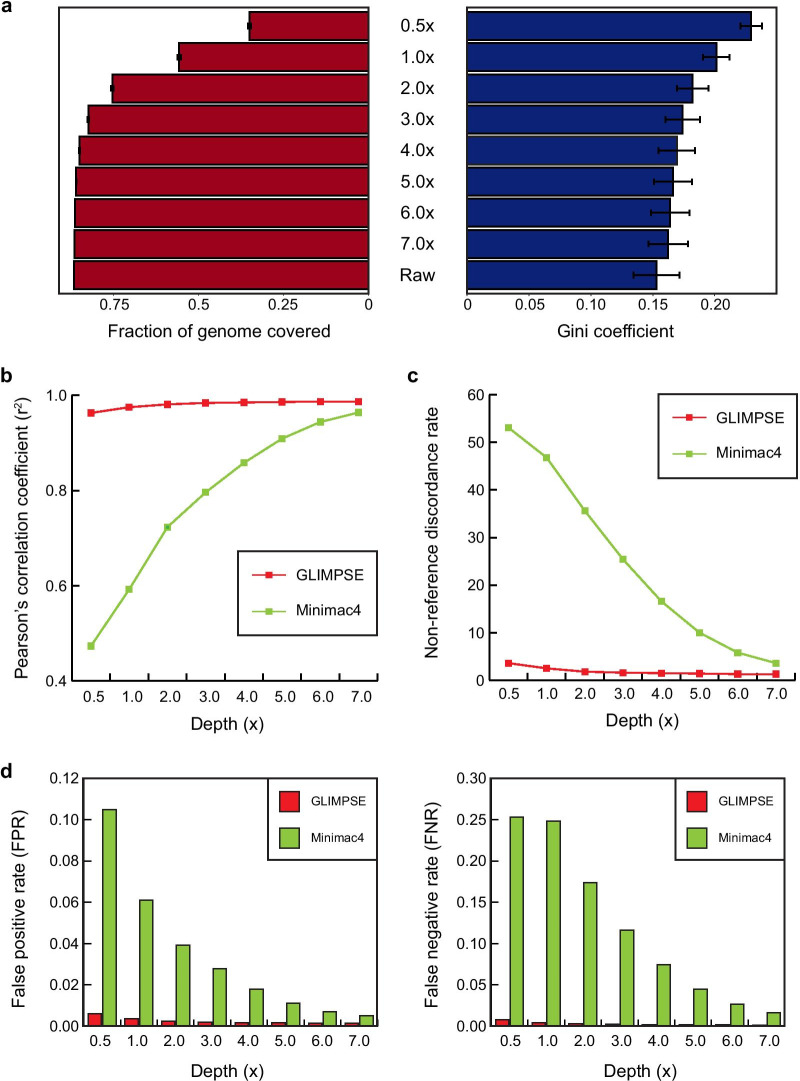
General sequencing statistics and genotype concordance between high-coverage WGS and LPS. a Across downsampled LPS and high-depth WGS, left graph shows fraction of whole-genome covered and right shows sequencing read uniformity, measured by Gini coefficients using Lorenz curve constructed with cumulative fraction of sequencing reads within the window size of 10 k base pair of genomic regions. Genotype concordance plots comparing eight high-coverage WGS and LPS constructed by downsampling WGS to low coverage ranging from 0.5 × to 7.0 × . Red and green color represent different imputation approaches; GLIMPSE and Minimac4, respectively. The x-axis represents downsampled depth. The y-axis represents imputation performances; b Pearson’s correlation coefficient (R2) and c Non-reference discordance rate. d Details of genotype concordances between high-coverage genotypes and imputed dosages. The rates of false positive (FPR) and negative (FNR) denote mismatches when reference allele in high-coverage but alternates in imputed LPS, and mismatches when alternate allele in high-coverage but reference in imputed LPS, respectively. The x-axis represents each LPS depth, and the y-axis represents a fraction of each concordance case