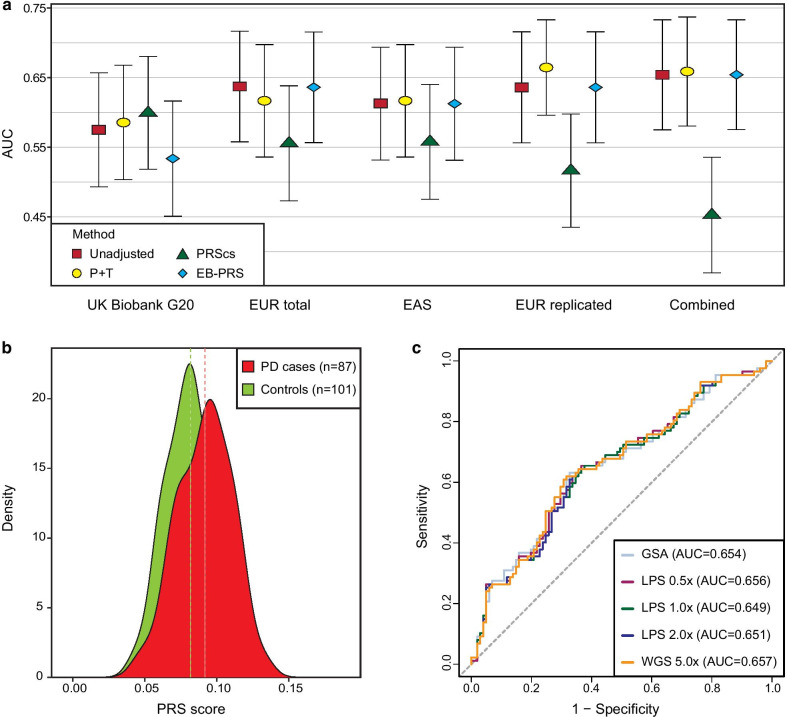
Fig. 3.
Assessment of PRS models based on SNP sets from GWAS in European and East Asian populations. a Evaluation of 5 different PRS models using 4 different PRS approaches based on data of GSA followed by imputation. The x-axis presents PRS models: UK Biobank G20; GWAS summary statistics of PD from the UK Biobank study of European populations, EUR total; 74 previously identified PD-associated SNPs in European populations, EAS; 11 genome-wide significant SNPs in a meta-GWAS of East Asians (P < 5.00 × 10–8), EUR replicated; 9 SNPs in EUR total that were replicated in a meta-GWAS (P < 1.00 × 10–5), and Combined; 16 SNPs of EAS and EUR replicated that were LD clumped. A total of 4 different approaches for PRS calculations were used: unadjusted, P + T, PRScs, and EB-PRS. The area under curve (AUC) with 95% confidence intervals are shown in the y-axis. b Score distributions of 87 PD cases and 101 controls using GSA based on the Combined set. Red color and green color represent PD cases and controls, respectively. Mean score values of each group were presented as dashed lines. c AUC of the Combined set using GSA, low-coverage WGS (5.0 × average) and downsampled LPS 0.5 × , 1.0 × and 2.0 ×