Fig. 1. Modification of SCC with Glc side-chains and GroP.
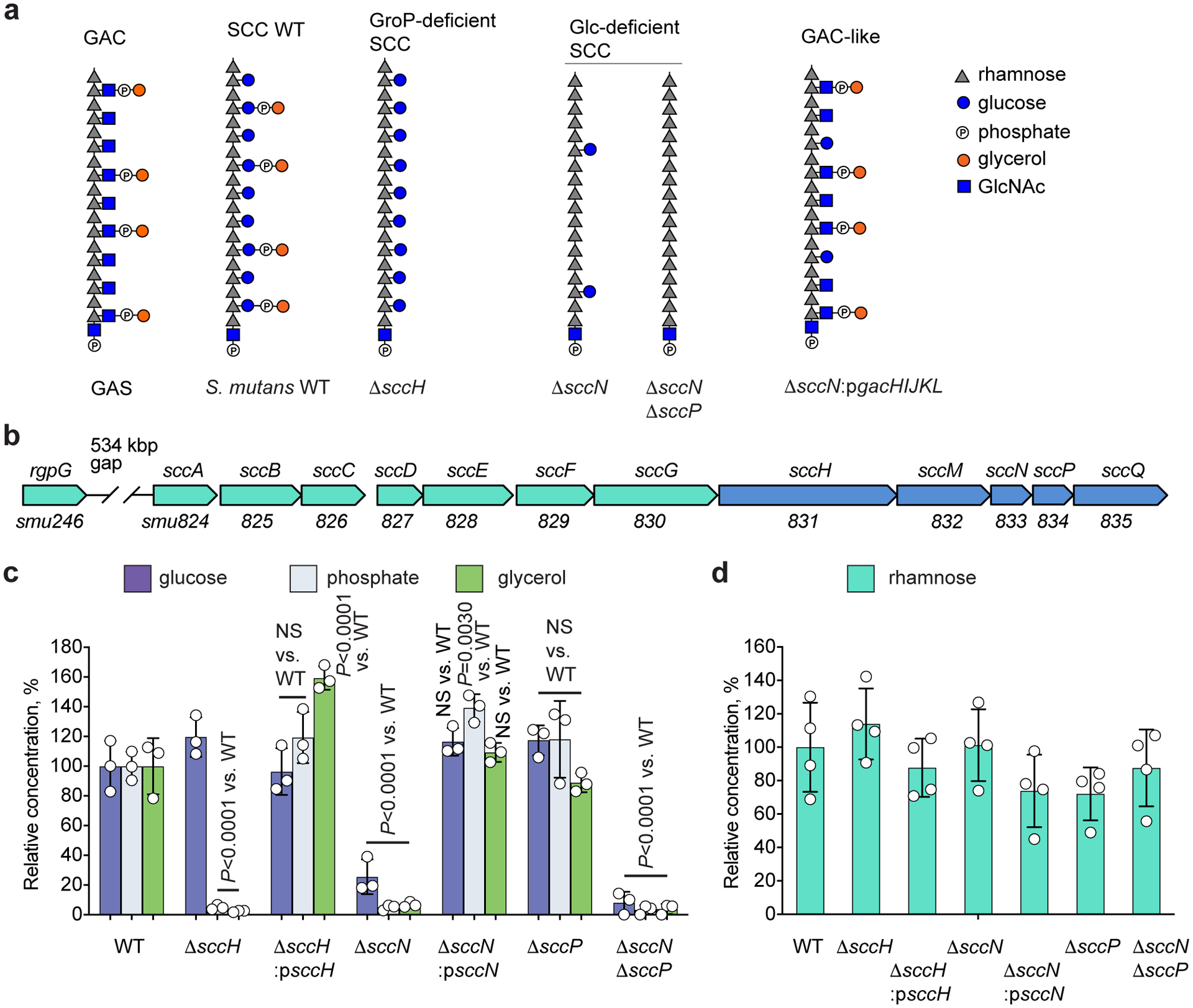
(a) Molecular model of cell wall polysaccharides isolated from GAS and S. mutans strains. Phosphate groups in the GAC and SCC structures are involved in the phosphodiester bond linking glycerol to the glycosyl side-chain. (b) Schematic representation of the SCC biosynthetic gene cluster. SCC gene cluster smu.824–835 was renamed sccABCDEFGHMNPQ21. (c) Composition analysis of SCCs isolated from S. mutans WT, ΔsccH, ΔsccH:psccH, ΔsccN, ΔsccN:psccN, ΔsccP, and ΔsccNΔsccP. The concentrations of Glc, phosphate, and glycerol are normalized to Rha content, and presented as a percentage of the ratios in the WT strain. Glc was analyzed by GC-MS method. Phosphate and glycerol were analyzed by colorimetric assays. Data are presented as mean values ± S.D., n = 3 biologically independent experiments. P values were calculated by 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. (d) Rhamnose content of S. mutans strains. Values expressed as a percentage of the WT values. The concentration of Rha was analyzed by GC-MS method. Data are presented as mean values ± S.D., n = 4 biologically independent experiments.
