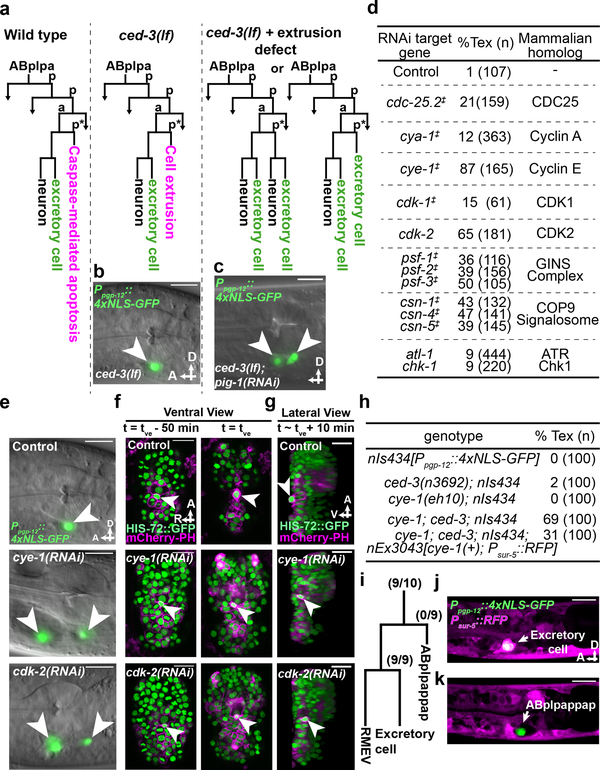
Figure 1. Cell-cycle genes control cell extrusion cell autonomously.
a, Sublineage diagram showing the fate of ABplpappap (*) in wild-type, ced-3(lf) and ced-3(lf)+extrusion-defective animals. b, c, Merged epifluorescence and Nomarski micrographs of the pharyngeal region of (b) nIs433[Ppgp-12::4xNLS-GFP]; ced-3(lf) and (c) extrusion-defective nIs433; ced-3(lf); pig-1(RNAi) animals (ref. 3). d, The percentages of animals with the Tex phenotype in ced-3(lf) animals after the indicated RNAi treatment. ‡, identified from screen shown in Extended Data Figure 1a; others identified from candidate RNAi screens. e, Merged epifluorescence and Nomarski micrographs of the pharyngeal region of nIs433; ced-3(lf) animals after the indicated RNAi treatment. f, g, Ventral and virtual lateral views of ced-3(lf); stIs10026[his-72::GFP]; nIs632[Pegl-1::mCherry::PH] embryos after the indicated RNAi treatment at the indicated time point. tve – time point of ventral enclosure. h, Percentage of animals of the indicated genotype displaying the Tex phenotype. i, Cell-lineage diagram showing number of animals with the Tex phenotype carrying the cye-1(+)-rescuing array nEx3043 in the indicated lineage or cell in 10 cye-1(lf); ced-3(lf); nIs434[Ppgp-12::4xNLS-GFP] animals. j, k, Two confocal fluorescence micrographs of one of 10 cye-1(lf); ced-3(lf); nIs434; nEx3043 genetic mosaic worms represented in (i). Arrowheads, excretory or ectopic excretory-like cells in (b, c, e); ABplpappap in (f, g). A, anterior; R, right; D, dorsal; V, ventral. Scale bars, 10 μm.