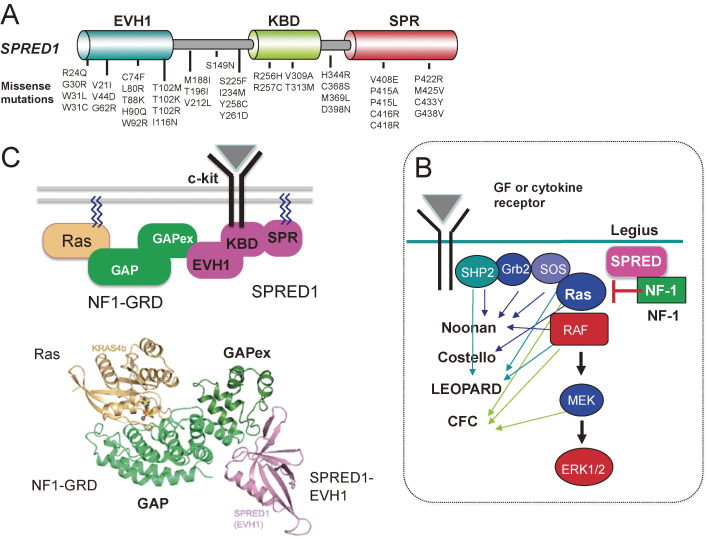
Figure 6.
SPRED functions and RASopathy. (A) Schematic structure of SPRED1 and major mutations found in Legius syndrome. (B) Detailed signaling pathways of the Ras-ERK pathway from the cytokine or growth factor (GF) receptors, and related RASopathy syndromes. Mutations in the components of this pathway are linked to syndromes, including: Cardio-Facio-Cutaneous (CFC), Costello, Legius, Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), Noonan, and LEOPARD syndromes. These syndromes share many clinical features such as distinct facial features, developmental delays, cardiac defects, growth delays, neurologic issues, and gastrointestinal difficulties. Not all components are shown in this figure. Please see Ref. 78 for details. (C) Model for the suppression of Ras activation by NF1 and SPRED1 complex. The SPRED1-EVH1 domain binds directly to the extended GAPex domain of NF1-GRD. SPRED1-KBD interacts with c-kit. SPR is palmitoylated and thus anchored in the membrane. The lower structure is the complex formed by Ras (brown), NF1-GRD (green), and SPRED1-EVH1 (pink) (modified from Refs. 80 and 86).