Figure 2. Near-infrared and far-red GEVIs and their representative applications.
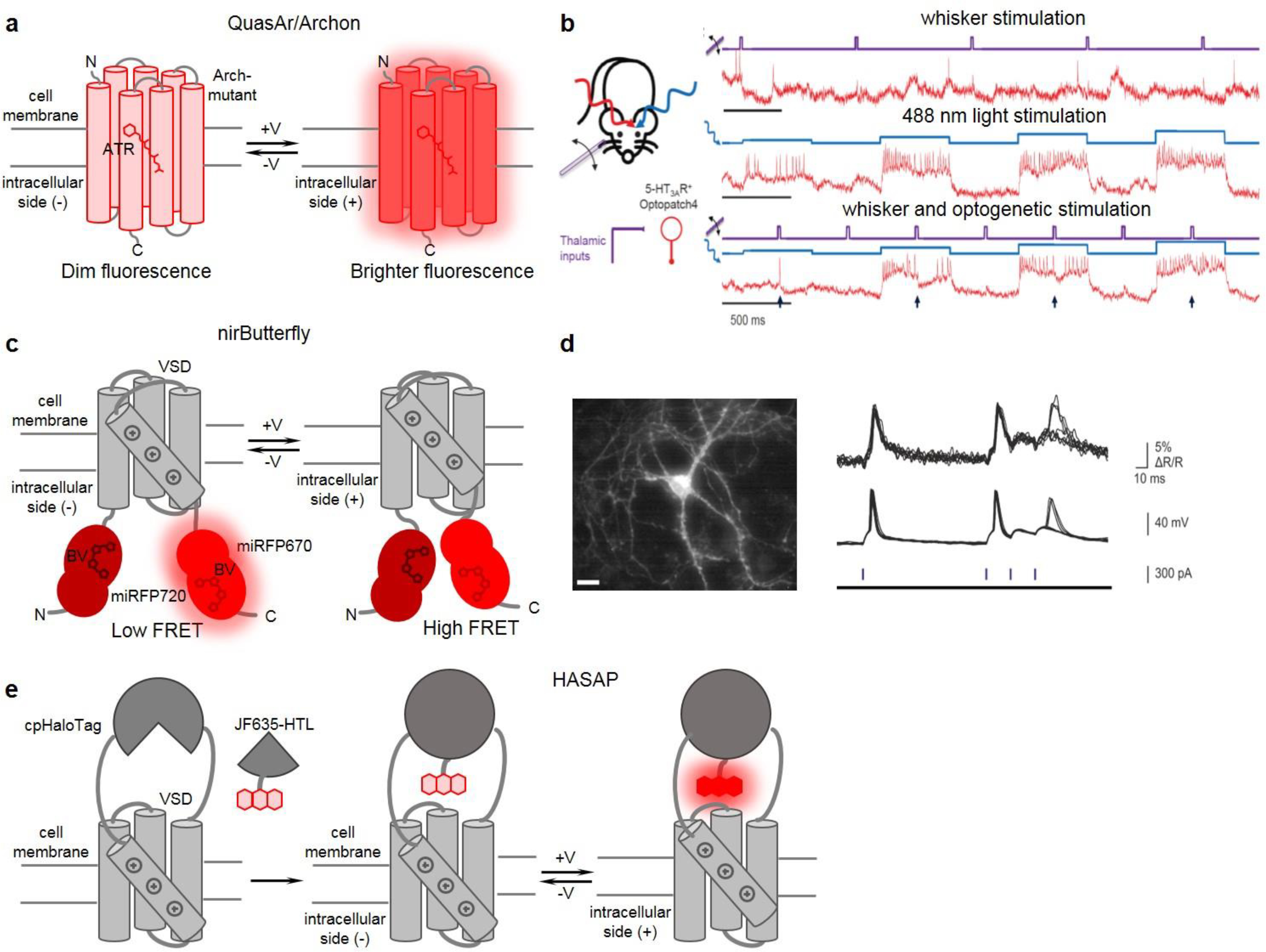
(a) Schematics of rhodopsin-based GEVIs of Archon/QuasAr series. (b) All-optical electrophysiology applied to optical dissection of neuronal excitation and inhibition in vivo. (left) Schematics of applied stimuli (whisker stimuli and single-cell optogenetic stimuli with 488 nm) and recording of SomArchon GEVI activity with 639 nm light. (right) Recordings from a single neuron showing SomArchon response to whisker stimuli (top), optogenetic stimuli (middle), and their combination (bottom). Whisker stimuli are in violet, optogenetic stimuli are in blue, and SomArchon GEVI responses are in red. Adapted, with permission, from57. (c) Schematics of nirButterfly FRET GEVIs. (d) nirButterfly in all-optical electrophysiology in vitro. (left) Fluorescence image of a neuron expressing nirButterfly. (right) nirButterfly response to CheRiff photocurrent-triggered action potentials and subthreshold depolarization. Optical signal (top), microelectrode recording (middle), pulses of 488 nm light (bottom). Adapted, with permission, from53. (e) Schematics of HASAP indicator as an example of a chemigenetic voltage indicator. (a, c, e) Arch-mutant: GEVI derived as Archaerhodopsin 3 mutant; ATR: all-trans retinal; BV: biliverdin; VSD: voltage sensing domains from voltage sensitive phosphatases; cpHaloTag: circular permutant HaloTag; JF635-HTL: synthetic rhodamine dye.
