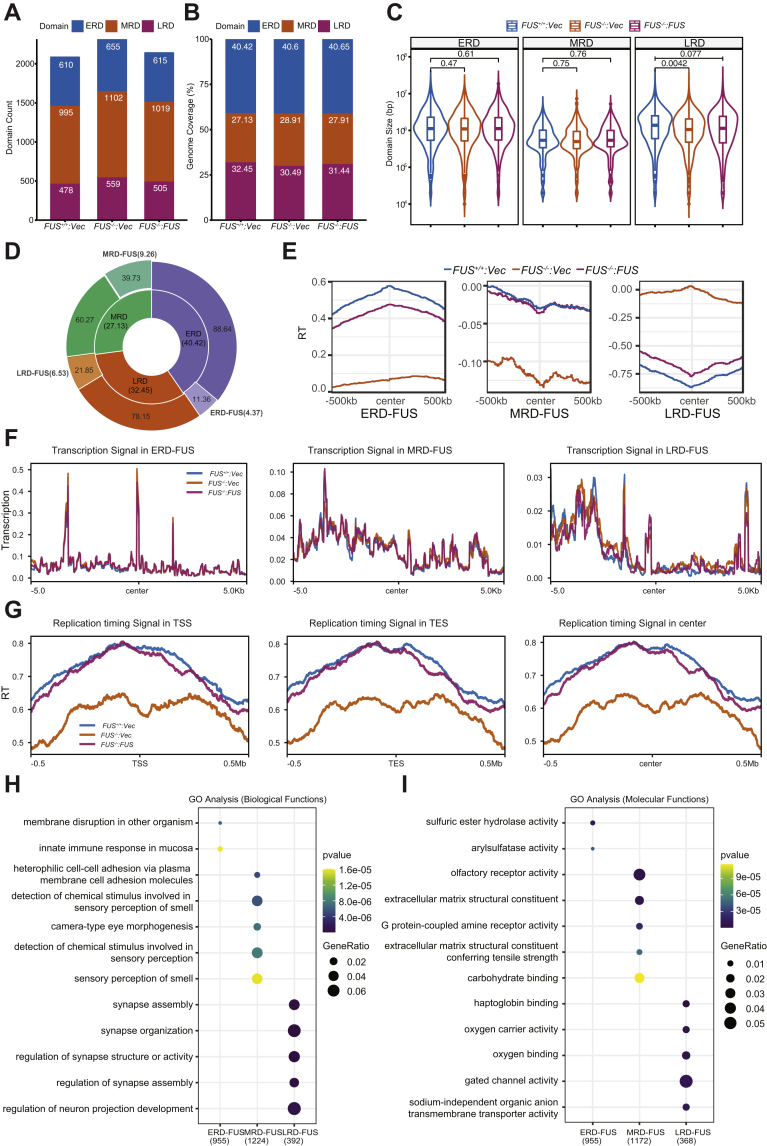
Figure 9.
Characterization of FUS-dependent replication domains (RDs).A, RT profiles were segmented into three states by nonsupervised package Segway as early RD (ERD), middle RD (MRD), and late RD (LRD). The domain numbers in each sample were plotted and labeled. The two biological replicates were merged for RD segmentation. B, percentages of genome coverage of RDs in each sample were calculated based on the segmentation. The values are percentages of each domain. C, the same RT domain sizes are compared among all the samples. The Student's t test was used for determination of significance. D, doughnut pie chart of FUS-dependent RD coverage. The percentage of each RD (ERD, MRD, and LRD; center pie) that is altered by FUS deficiency (FUS-dependent RDs) is shown in the outside layer, and the total percentage of each FUS-dependent RDs (ERD-FUS, MRD-FUS, and LRD-FUS) are calculated and shown in parentheses. The percentage was calculated based on the genome coverage. E, RT signal enrichment analysis of FUS-dependent replication domains in the samples. The average domain size is ∼106 bp C, and ∼0.5 × 106 bp flanking the midpoint was used for signal enrichment. Heat map results of RT signal enrichment of changing ERD, MRD, and LRD in all individual samples were shown in Fig. S9, E–G. F, transcription signal in the centered FUS-dependent RDs. Transcription signal was normalized with CPM by STAR. G, RT signal enrichment around TSS, TES, and center of FUS-regulated gene regions across a ±0.5 Mb window. RT signal was calculated by log2 ratio of S/G1 samples in 20 kb bin after CPM normalization and followed with Z score normalization. Only FUS-regulated genes (listed in Table S3) annotation was used. H, Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment in biological function level of FUS-dependent RDs. The FUS-dependent RDs were extended 3000 bases in both ends, and then, the gene list under the extended FUS-dependent RDs was extracted and used for GO analysis. I, GO analysis in molecular function level of extended FUS-dependent RDs. FUS, fused in sarcoma; RT, replication timing; TES, transcription end site; TSS, transcription start site.