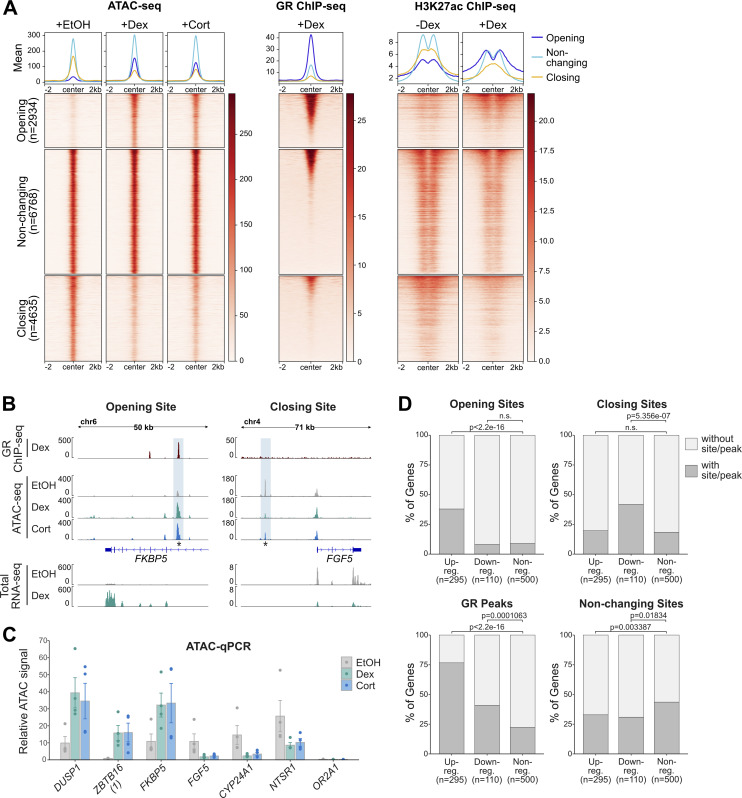
Figure 1. Integrated analysis of genome-wide changes in chromatin accessibility and transcript levels upon glucocorticoid receptor (GR) activation.
(A) Heat map visualization and mean signal plot of ATAC-seq (normalized), GR ChIP-seq (RPKM-normalized; 100 nM Dex, 3 h; data from reference 37), and H3K27ac ChIP-seq (RPKM-normalized; ±100 nM Dex, 4 h; data from reference 41) read coverage in A549 cells at sites of increasing (“opening”), non-changing (“non-changing”), and decreasing (“closing”) chromatin accessibility upon hormone treatment (±2 kb around center). Heat maps are sorted by GR ChIP-seq signal in descending order. For ATAC-seq, cells were treated with EtOH vehicle (20 h), Dex (100 nM, 20 h) or Cort (100 nM, 20 h). (B) Genome browser visualizations of the FKBP5 and FGF5 loci in A549 cells showing GR ChIP-seq (100 nM Dex, 3 h; RPKM-normalized; data from reference 37), ATAC-seq (normalized) and RNA-seq (RPKM-normalized, merge of three replicates) signal tracks. For ATAC-seq experiments, cells were treated with EtOH (20 h), Dex (100 nM, 20 h) or Cort (100 nM, 20 h). For RNA-seq, cells were treated as detailed in Fig 3A, receiving a vehicle control treatment (4 h), followed by a 24-h hormone-free period and a subsequent 4 h Dex- (100 nM) or EtOH-treatment (“−−”: EtOH, “−+”: Dex). Opening/closing site is highlighted with blue shading. The asterisk marks the position of the qPCR primers for the analysis shown in (C). (C) ATAC-qPCR at sites opening or closing upon hormone treatment near indicated genes in A549 cells. Cells were treated with EtOH (20 h), Dex (100 nM, 20 h), or Cort (100 nM, 20 h). Mean ATAC signal (normalized to gDNA) ± SEM (n = 4) is shown. (D) Stacked bar graphs showing the percentage of genes in A549 cells of each category (up-regulated, down-regulated, and nonregulated) that have at least one peak/site for each type (opening, closing, and non-changing sites and GR peaks) within ±50 kb around the transcription start site. GR peaks represent the intersect of peaks called in both replicates (data from reference 37). P-values were calculated using a Fisher’s exact test. NS, not significant.