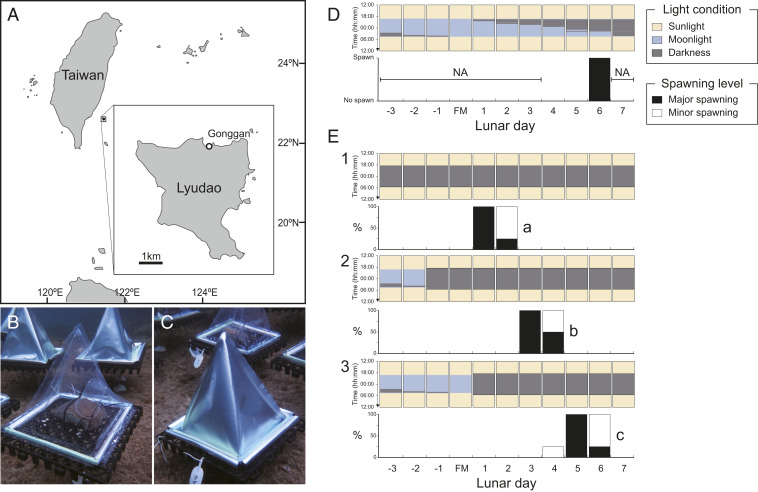
Fig. 1.
Spawning day of D. speciosa in the field manipulation experiment. (A) Study location at Lyudao (Green Island), Taiwan. The white dot indicates Gonggan, where D. speciosa fragments were collected and the field observation and experiment were conducted. (B) An egg trap in a transparent plastic bag and (C) an egg trap in an aluminum foil bag. (D) Spawning in natural populations of D. speciosa (>10 colonies) at the study location and (E) spawning of D. speciosa fragments under the moonlight-blocking treatment commencing at 3 d before the full moon (panel 1), 1 d before the full moon (panel 2), and 1 d after the full moon (panel 3). Black bars indicate major spawning (>hundreds of eggs), and white bars indicate minor spawning (several eggs) in four replicate fragments. Note that “NA” indicates no observation. Different letters in the panels in E indicate significant differences between the treatments (ANOVA and Tukey HSD test; P < 0.001). For detailed results of statistical analysis, refer to SI Appendix, Table S2.