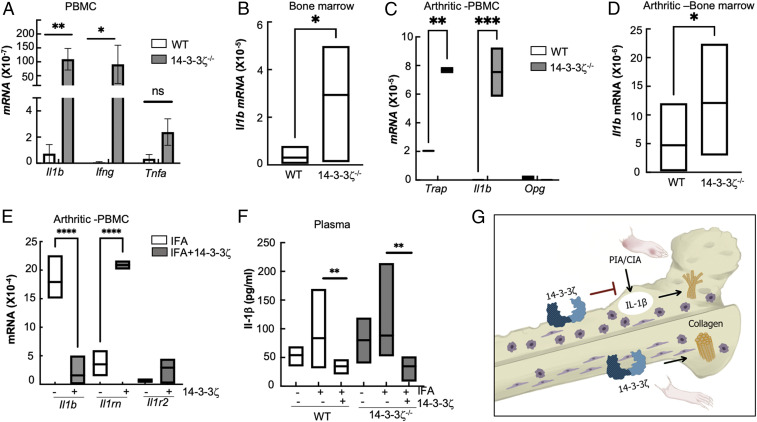
Fig. 7.
14-3-3ζ supplementation interferes with IL-1β signaling. (A) Expression of proinflammatory cytokines, including Il1b, Ifng, and Tnfa, was measured in the circulating immune cells of WT and 14-3-3ζ KO–naïve animals using RT-qPCR. (B) The Il1b transcript in the bone marrow of naïve 14-3-3ζ KO as compared with WT using RT-qPCR. (C) Expression of Il1b, Trap, and Opg, was measured in the circulating immune cells of WT and 14-3-3ζ KO arthritic animals using RT-qPCR. (D) The Il1b transcript in the bone marrow of arthritic 14-3-3ζ KO as compared with WT animals using RT-qPCR. (E) Expression of Il1b, Il1rn, and Il1r2 was measured in PBMC of 1 wk postimmunization in the 14-3-3ζ KO animals that received IFA alone or with 14-3-3ζ protein. (F) IL-1β was measured in the plasma of WT and KO–naïve or arthritic animals using quantitative ELISA. (G) Overall model depicts that the absence of 14-3-3ζ results in severe inflammation and bone damage; mainly, increased IL-1β and reduced collagen levels are observed in the naïve and IA-affected animals. Immunization with 14-3-3ζ interferes with IL-1β and promotes collagen synthesis to prevent inflammation and bone damage. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005, and ****P < 0.0001.