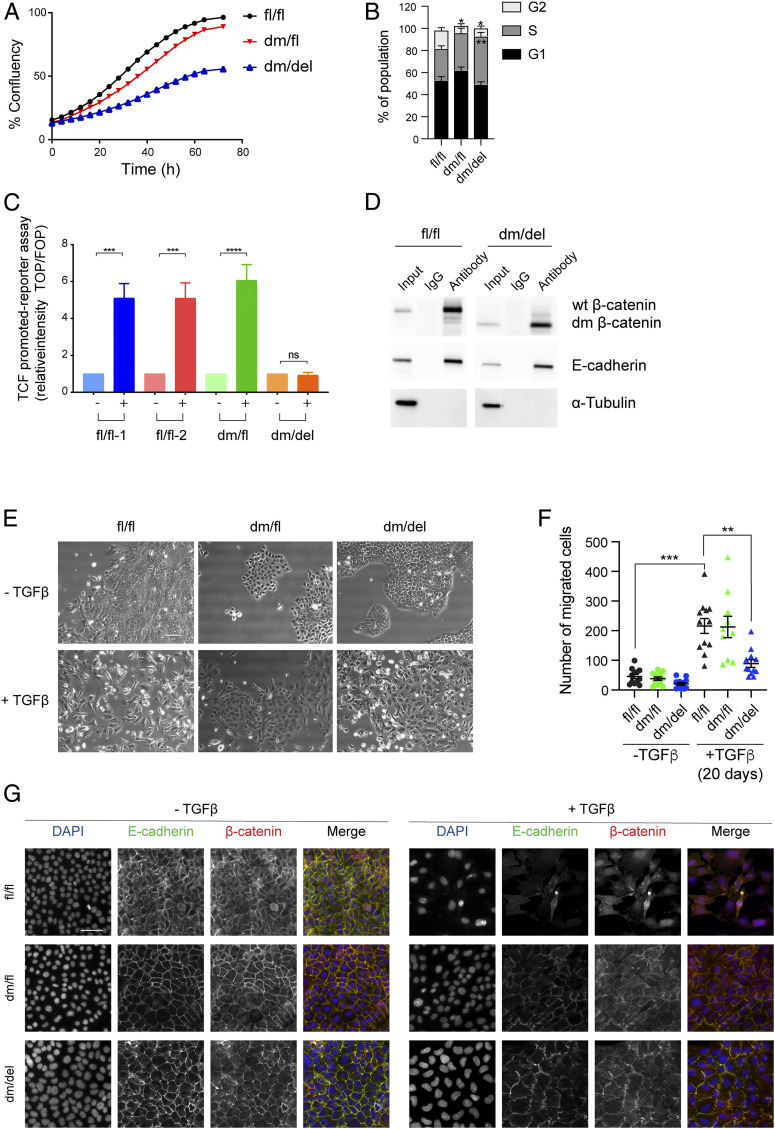
Fig. 3.
Loss of β-catenin cofactor binding impairs Wnt signaling activity, tumor cell proliferation, and EMT. (A) Comparison of the growth curves of mammary tumor cell lines expressing wild-type (fl/fl) β-catenin, one wild-type and one mutant allele of β-catenin (dm/fl), or only the mutant allele of β-catenin (dm/del). (B) Mammary tumor cells expressing the dm version of β-catenin (dm/del or dm/fl) are stalled in the S phase of the cell cycle. Cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry quantified from the data shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S4C. Statistical analysis was performed using ordinary one-way ANOVA multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (C) Wnt-induced β-catenin–mediated transcriptional activity as determined by superTOPflash/ superFOPflash promoter reporter assay. Cell lines derived from tumors of the various genotype MMT-PyMT transgenic mice were treated with Wnt3a, and Wnt-dependent luciferase activity was determined. fl/fl-1 and fl/fl-2 = two independent cell lines expressing wild-type β-catenin; dm/fl = cell line expressing wild-type β-catenin and the dm β-catenin; dm/del = cell line expressing only the dm version of β-catenin. The results represent four independent experiments. Data are displayed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using ordinary one-way ANOVA multiple comparison test. ***P < 0.005; ****P < 0.001; ns, not significant. (D) The mutant form of β-catenin still binds E-cadherin at the adhesion junctions. Coimmunoprecipitation using anti–β-catenin or rabbit IgG control in cell lines expressing wild-type (fl/fl) or the dm form of β-catenin (dm/del) and subsequent immunoblotting against β-catenin, E-cadherin, and α-tubulin as a loading control for the input. (E) Mammary tumor cell lines expressing mutant β-catenin are partially impaired in undergoing a TGF-β–induced EMT. Wild-type β-catenin–expressing cell lines (fl/fl) readily undergo TGF-β–induced morphological changes to a mesenchymal cell phenotype, while dm β-catenin–expressing cells (dm/fl or dm/del) only form filopodia without showing any specific mesenchymal cell morphology. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (F) Migration of mammary tumor cells expressing wild-type β-catenin (fl/fl), cells expressing one allele of β-catenin and one allele of dm β-catenin (dm/fl), and cells expressing exclusively dm β-catenin (dm/del) in the absence of TGF-β or upon treatment with TGF-β for 20 d was determined in a Transwell migration assay. Data are displayed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using ordinary one-way ANOVA multiple comparison test. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005. (G) Immunofluorescence staining for β-catenin (red) and the EMT-related marker E-cadherin (green) reveals a reduced expression of the epithelial markers E-cadherin at the cell membrane in wild-type β-catenin–expressing cells (fl/fl), while in dm β-catenin–expressing cells (dm/fl and dm/del), E-cadherin and β-catenin are maintained at the cell junctions. DAPI was used to visualize nuclei. (Scale bar, 50 μm.)