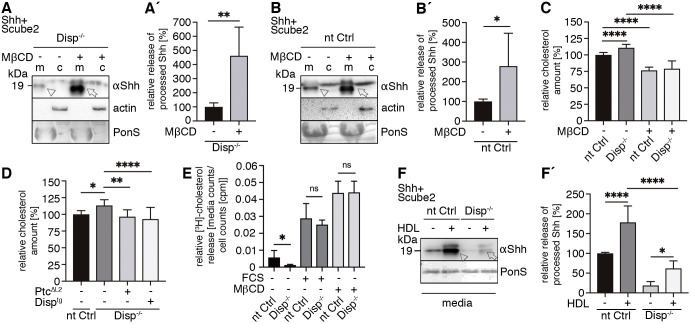
Fig. 5.
Disp-deficient cells contain increased membrane cholesterol, and cholesterol depletion increases Shh shedding. (A–B′) The membrane-cholesterol-depleting drug MβCD enhances Shh shedding from Disp−/− cells (A,A′) and nt Ctrl cells (B,B′). Solubilized Shh in the absence or presence of MβCD is indicated by an arrowhead or an arrow, respectively (c, cellular Shh; m, Shh released into the medium). In A and B, anti-β-actin blots and Ponceau S staining of residual serum albumin (PonS) serve as loading controls. Data in A′ and B′ are mean±s.d. n=6 in A′, n=5 in B′. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (two-tailed unpaired t-test). (C) Quantified relative free cholesterol content in nt Ctrl and Disp−/− cells in the presence or absence of MβCD. Data are mean±s.d. nt Ctrl and Disp−/−, n=29; both MβCD-treated groups, n=9. ****P<0.0001 (one-way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparison post hoc test). (D) Quantified relative free cholesterol content in nt Ctrl cells, Disp−/− cells, and Disp−/− cells expressing PtcΔL2 or Disptg. Data are mean±s.d. nt Ctrl n=14, all Disp−/− groups n=13. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001 (one-way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparison post hoc test). (E) The indicated cell lines were loaded with [3H]-cholesterol for 48 h then washed, and cholesterol release into serum-depleted medium (FCS−) or medium with 10% FCS (FCS+) was measured for 3 h. [3H]-cholesterol signals in media are expressed relative to cellular counts. MβCD treatment (MβCD+; 1 mg/ml) served as a positive control. FCS− MβCD− n=6, FCS+ MβCD− n=5, FCS− MβCD+ n=3 for each cell line. Data are mean±s.d. *P<0.05; ns, not significant (two-tailed unpaired t-test). (F) HDL enhances Shh release into the medium from nt Ctrl cells (arrowhead) and to a lesser degree from Disp−/− cells (arrow). Ponceau S staining of residual serum albumin (PonS) serves as loading control. (F′) Quantification of relative processed Shh release, as shown in F. Data are mean±s.d. nt Ctrl groups n=6, Disp−/− groups n=5. *P<0.05, ****P<0.0001 (one-way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparison post hoc test).