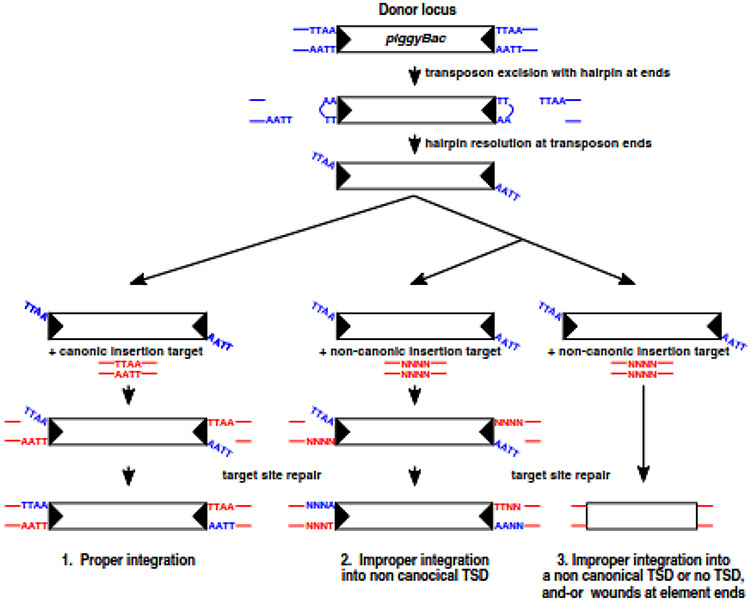
Fig. 6.
Signatures of proper and improper DNA integration in a pble transposition system (graphic derived from Figure 1 in https://doi.org/10.1101/015289). piggyBac transposition is initiated by nicks at the transposon ends. The exposed 3’OHs then attack the complementary strand 4 nt inside the flanking donor DNA to form the hairpins on the transposon end. The hairpins on the transposon ends are nicked at the 3’ transposon ends. In a proper integration event (pathway 1), transposon ends thereafter attack the TTAA target sequence at staggered positions, forming covalent links between the 3’ end of the transposon and the 5’ ends of the target site. The single strand gap between the 3’ ends of the target DNA and the 5’ ends of the transposon are repaired to generate the four bp TTAA target sequence duplication. In an improper integration event, transposon ends thereafter attack a random target sequence at staggered positions, forming covalent links between the 3’ end of the transposon and the 5’ ends of the target site. The single strand gap between the 3’ ends of the target DNA and the 5’ ends of the transposon are repaired to generate a non-canonical target sequence duplication (pathway 2). This process can also lead to wounds at transposon ends (pathway 3).