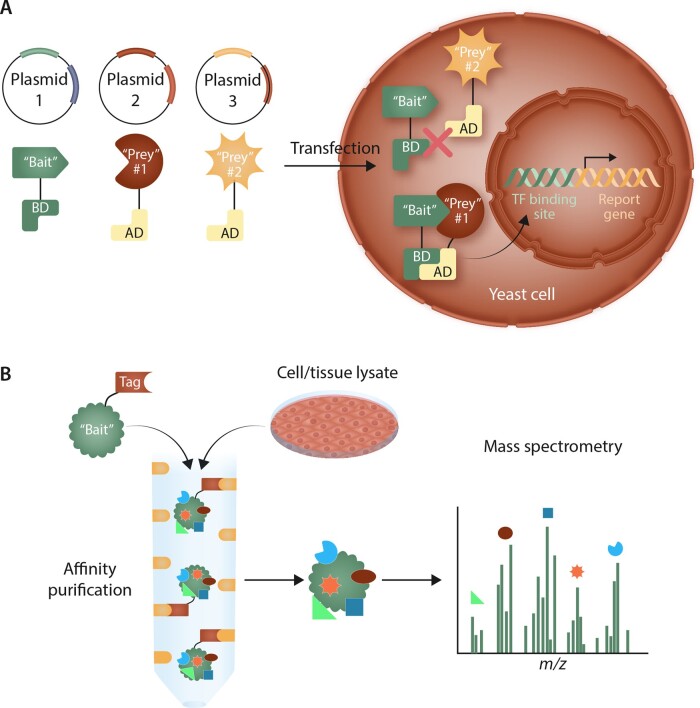
Figure 2.
High-throughput methods for determining protein-protein interactions. (A) In the yeast two-hybrid system, a plasmid is created expressing a ‘bait’ protein linked to the DNA binding domain (BD) of a transcription factor (TF) required for expression of a reporter gene. Various ‘prey’ proteins are then linked to the activation domain (AD) of this TF in separate plasmids. Plasmids are co-transfected in pairs into yeast cells. If the ‘bait’ and ‘prey’ proteins interact, the BD and AD domains of the TF will be in close enough proximity to translocate to the nucleus and initiate reporter gene expression. If the ‘bait’ and ‘prey’ do not interact, the reporter gene will not be expressed. (B) In co-complex discovery, a ‘bait’ protein is linked to a tag and incubated with target cell or tissue lysates to allow ‘prey’ proteins to associate. The ‘bait’-‘prey’ complexes are isolated through affinity purification utilizing the linked tag. The ‘prey’ proteins can then be identified using mass spectrometry.