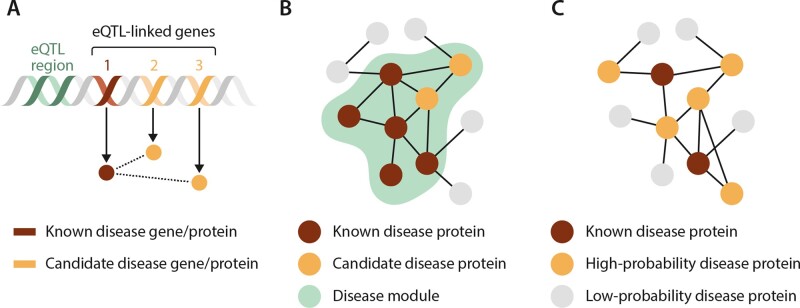
Figure 3.
Network-based methods to predict disease genes. (A) Linked genetic elements, for example through shared expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) containing a known disease gene, have increased probability that other genes within the linkage interval contribute to the disease process. Linkage methods can be utilized to uncover these candidate disease genes and proteins. (B) Disease modules identify network regions that contribute to a disease. Proteins contained within these network elements can be investigated as candidate disease proteins through methods such as the seed connector algorithm. (C) Diffusion propagation methods start with known disease proteins and then assign probabilities to proteins in the interactome based on the likelihood they are associated with the disease. This analysis is based on frequency of candidate proteins’ interactions with and network distance from the known disease proteins. Adapted from ref.6 with permission.