Figure 2.
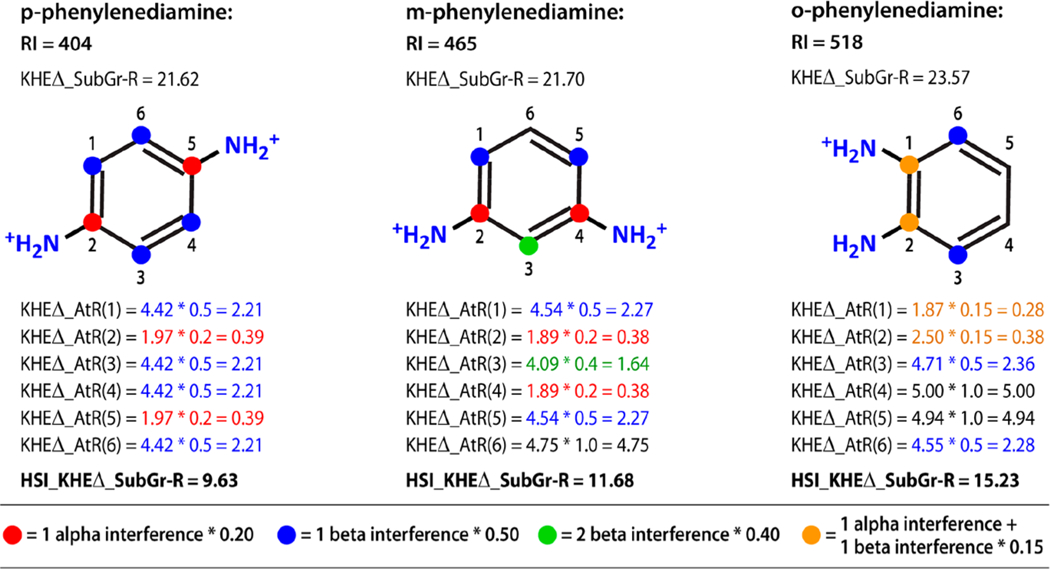
Calculation of hydrophilic steric interference adjustment for the lipophilic subgraph in three phenylenediamine isomers. The KHEΔ_AtR values are adjusted to take into account the steric interference of dispersion interactions caused by hydrophilic atoms associated with solvent. The interference coefficients are given in the color coded key and are based on the count of alpha and beta hydrophilic atoms. The KHEΔ_AtR values do not vary nearly as much as RI and explain only 76% of RI variance. Following the steric interference adjustment, the HSI_KHEΔ_SubGrAtR values explain 96% of RI variance. This ortho, meta, and para series of isomers illustrate that when hydrophilic atoms are close together relative to the lipophilic subgraph, the lipophilic subgraph is more exposed resulting in a longer retention time. The o-phenylenediamine isomer has a longer retention not only because of greater lipophilic subgraph exposure but also because an internal hydrogen bonding configuration has been introduced and because the major microspecies is only +1.
