Figure 2. Mechanisms of microbiota-host interactions promoting tumorigenesis.
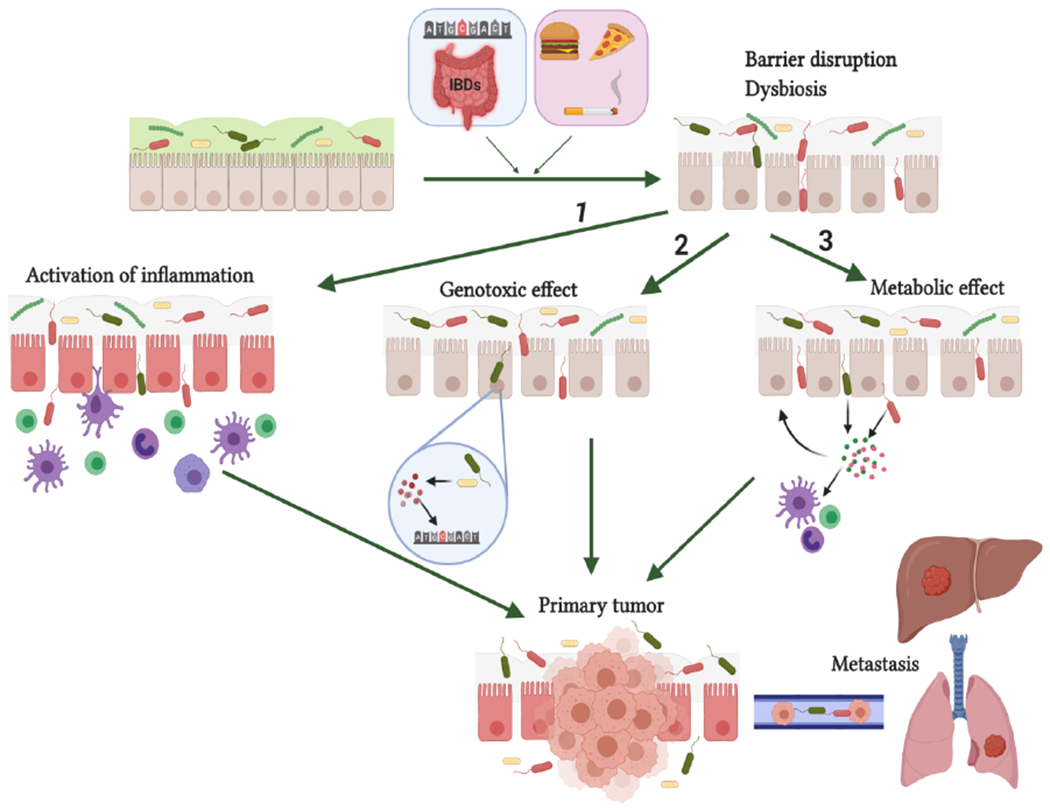
Non-modifiable (genetic) and environmental factors promote intestinal epithelial barrier disruption and dysbiosis. Barrier dysfunction causes bacterial penetration through the epithelium and their interaction with host cells by several mechanisms: (1) immune cell activation and triggering of pro-tumorigenic inflammation; (2) Epithelial cell DNA damage by bacterial toxins or bacteria-induced genotoxic products (e.g. ROS) ; (3) modulation of immune, stromal and cancer cell function through the effect of bacterial metabolites acting locally or distantly. Figure was produced using BioRender platform.
