Figure 1.
Metoprolol Disrupts COVID-19–Associated Exacerbated Lung Inflammation
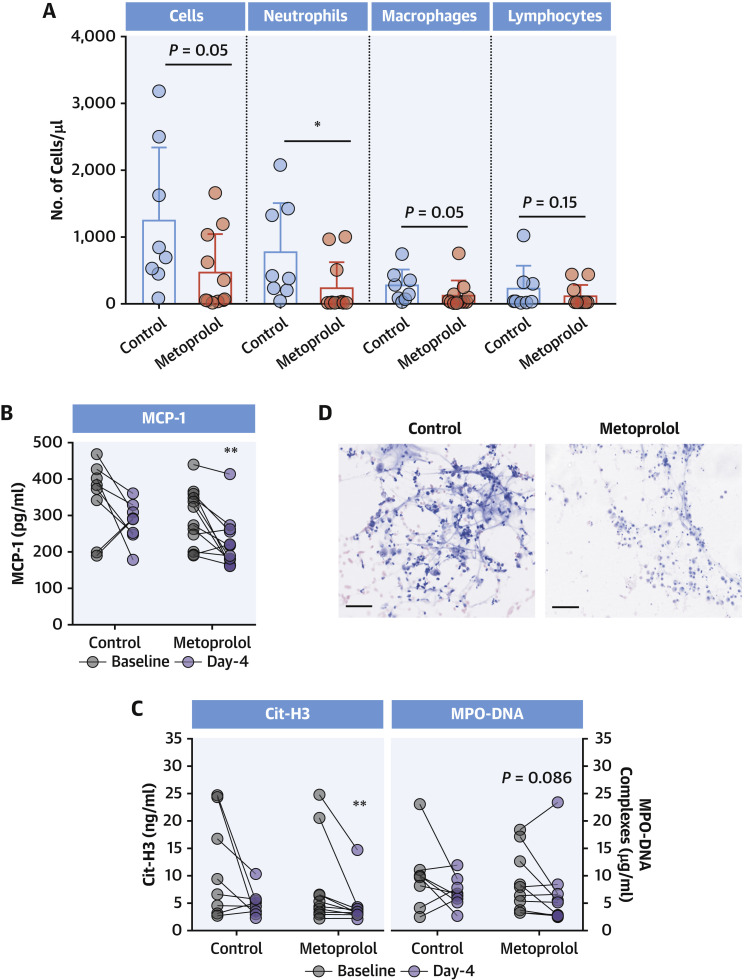
(A) Day 4 inflammatory cell populations in BAL from control and metoprolol-treated severe COVID-19 patients. Dots represent individuals and bars and error bars show mean values (boxes) ± SD (error bars). ∗P < 0.05 by unpaired Student's t-test. (B) Attenuation of MCP-1 in cell-free BAL from metoprolol-treated patients. (C) Attenuation of neutrophil hyperactivation biomarkers (Cit-H3 and MPO-DNA complexes) in cell-free BAL from metoprolol-treated patients. Data are presented as individuals’ (dots) paired data between days 1 and 4. ∗∗P < 0.01 by paired Student's t-test. (D) Representative images of Giemsa-stained BAL samples from control and metoprolol-treated patients at day 4. Scale bar, 50 μm. Control, n = 8; metoprolol, n = 12. BAL = bronchoalveolar lavage; Cit-H3 = citrullinated histone-3; COVID-19 = coronavirus disease-2019; MCP = monocyte chemoattractant protein; MPO = myeloperoxidase.