Figure 3:
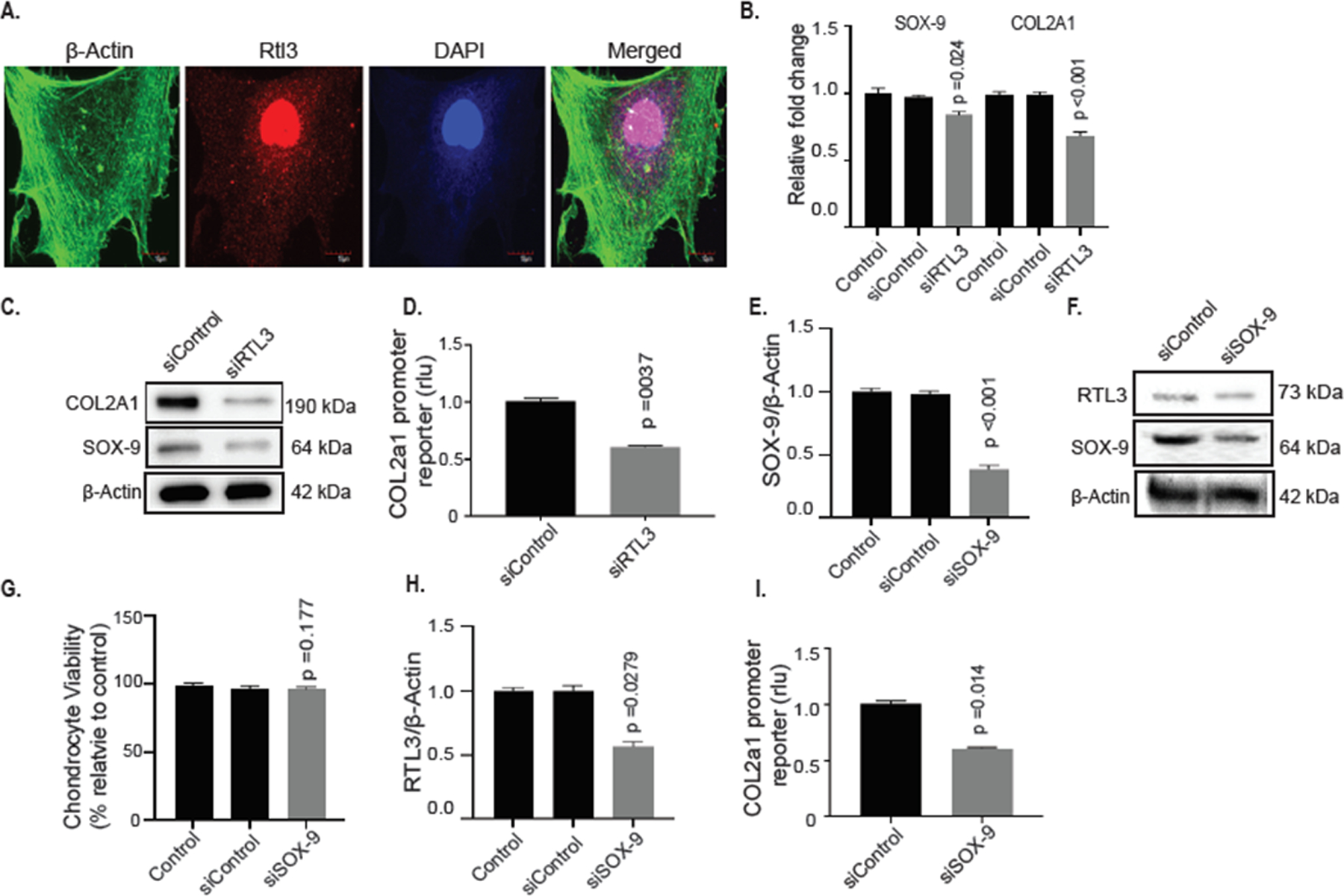
RTL3 co-localized to the nucleus in primary chondrocytes and depletion significantly reduced SOX-9 and COL2A1 mRNA and protein levels and siRNA-mediated depletion of SOX-9 negatively affects RTL3 expression in human chondrocytes. (A) Immunofluorescent staining with anti-RTL3 antibody (#NBP2–30741) followed by ActinGreen™ 488 ReadyProbes Reagent (#R37110) for 15 minutes and results demonstrated RTL3 nuclear co-localization. siRNA-mediated depletion of RTL3 significantly reduced SOX-9 and COL2A1 mRNA (B) and protein levels (C) and reduced the activity of the COL2A1 promoter reporter (D). Depletion of SOX-9 via a validated siRNA successfully reduced SOX-9 mRNA (E) and protein (F) levels in SOX-9-depleted chondrocytes without negatively affecting cell viability (G). siRNA-mediated depletion of SOX-9 significantly reduced RTL3 mRNA (H) and protein (F) levels and reduced the activity of the COL2A1 promoter reporter (I) levels of SOX-9 (E) and COL2A1 (F) as well as protein levels (G) were reduced as well as COL2A1 promoter reporter activity (H). Ectopic expression of RTL3 in HEK-293T cells increased COL2A1 promoter reporter activity in a dose-dependent manner (I) and increased SOX-9 (J) and COL2A1 (K) mRNA expression.
