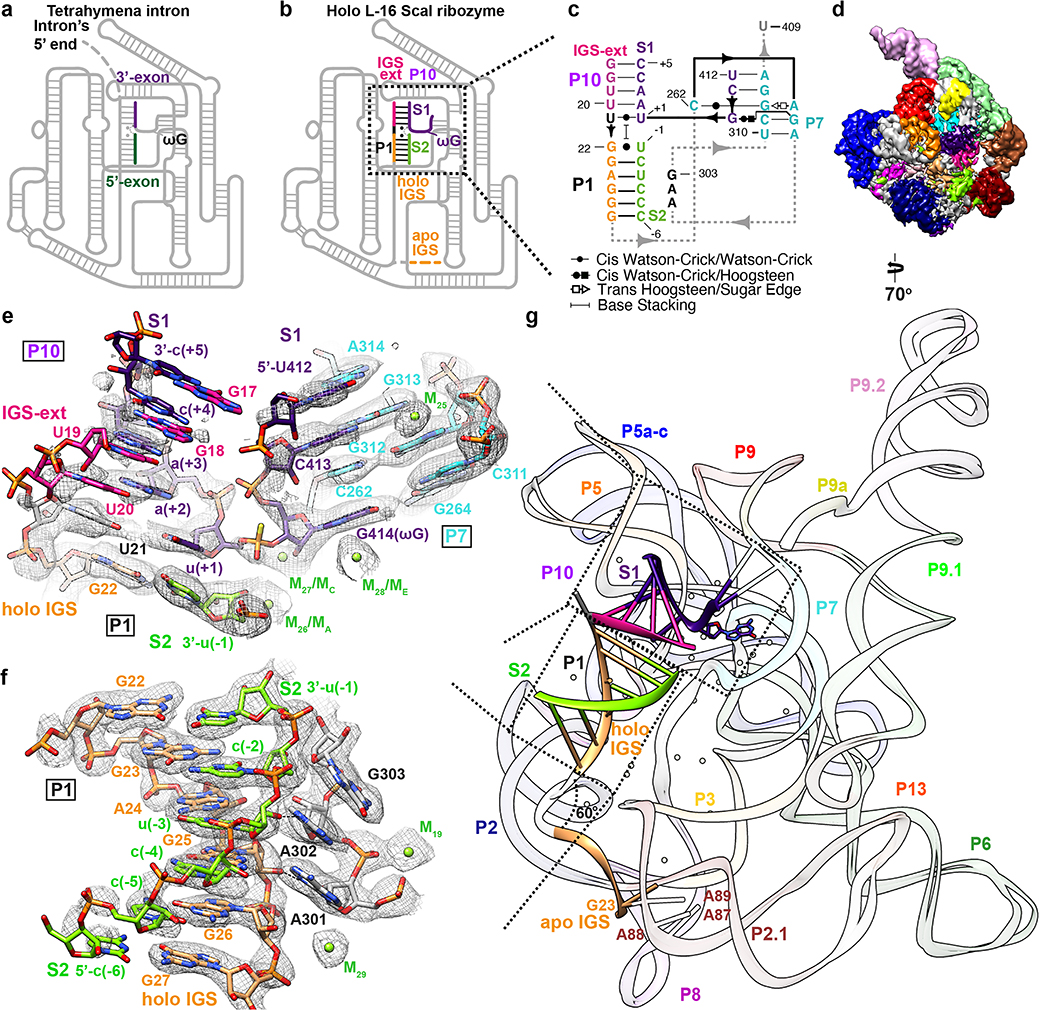
Figure 3. Cryo-EM structure of the holo L-16 ScaI ribozyme reveals docked P1-P10 and a substantial conformational change of IGS that mimics the second step of splicing.
Schematic illustrations of (a) the Tetrahymena intron in the second step of splicing and (b) the holo L-16 ScaI ribozyme mimicking the reaction in (a). (c) Secondary structure of the docked P1-P10 in the catalytic site. (d) Cryo-EM map of the holo L-16 ScaI ribozyme colored following the secondary structure. (e) Substrate S1 (dark purple) forms P10 with the IGS extension (deep pink), P7 extension with G313 and A314 (cyan), and occupies the guanosine binding site, visualized at 0.9σ threshold. (f) Substrate S2 (chartreuse) and IGS (sandy brown) forms P1, visualized at 1σ threshold. (g) Superposition of the apo and holo structure reveals conformational change of IGS from a substrate-free site close to A87, A88, A89. Dashed arrows in (a) and (b) indicate nucleophilic attack direction of the second step of splicing, dashed line indicates hydrogen bond.