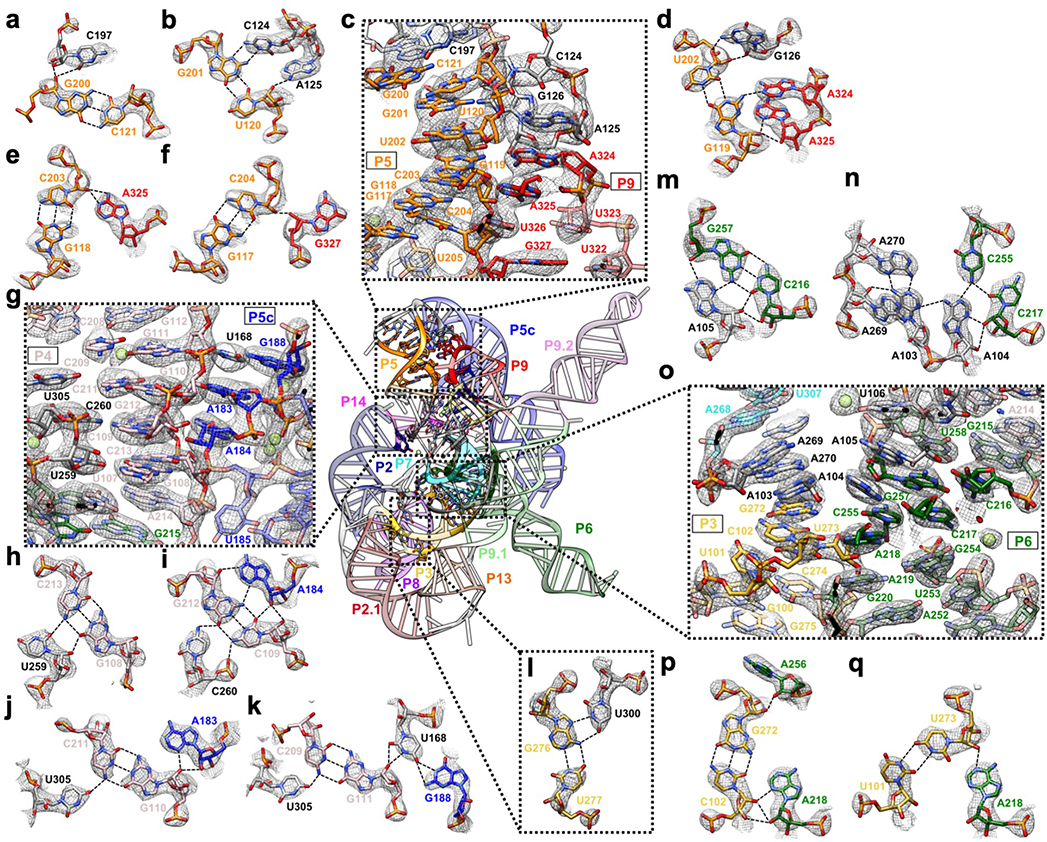
Extended Data Figure 4. Detailed tertiary interactions in the core region of the Tetrahymena ribozyme.
(a-f) The P5-J5/5a-L9 region has highly structured J5/5a junction in previous structures12,15. The cryo-EM structure shows tertiary interactions of (b) C124 and A125, (d) G126, (a) C197 and (d) A324, (e) A325, (f) G327 in the minor groove of P5. (g-k) Previous studies have identified A183 and A184 in A-rich bulge of the metal core, U259 and C260 from J6/7, U305 from J8/7 to be conserved and essential for catalytic site formation and splicing reactions52–58. The cryo-EM structure shows (h) U259, (i) C260, and (j-k) U305 stack continuously and interact with P4 base triples. (k) U168 from P5c stacks on the A-rich bulge and interacts with P4 in the minor groove, while pairing with G188 in P5a. (l) The Hoogsteen base triple U277-A97-U300 found to be essential for substrate helix recognition59. (m-q) In the P3-J3/4-P6-J7/3 region, A-rich J3/4 and J7/3 were previously found to interact with P6 in Azoarcus ribozyme17,60. Base triples formed by J3/4 were critical for catalysis52,57,58,61, and alterations in these regions result in RNA misfolding28,62. In the cryo-EM structure, (n) A104 and (m) A105 form A-minor interactions with P6, whereas (n) A103 and A104 join A269 and A270 from J7/3 to form an adenosine cluster. The proposed A103-U271 reverse-Hoogsteen pair is not found, instead we observed a noncanonical A103-A270 pair61. (p-q) The previously observed A-platform of A218-A219 is disrupted in the cryo-EM structure with P3 present12,30. A218 forms two A-minor interactions with C102-G272 and U273-U101 from P3, which also supports the conservation of this C-G pair in group Ib introns61. Black dashed line indicates hydrogen bond. The cryo-EM maps of all subpanels are visualized at 1σ threshold except for (c, g and o) at 1.5σ.