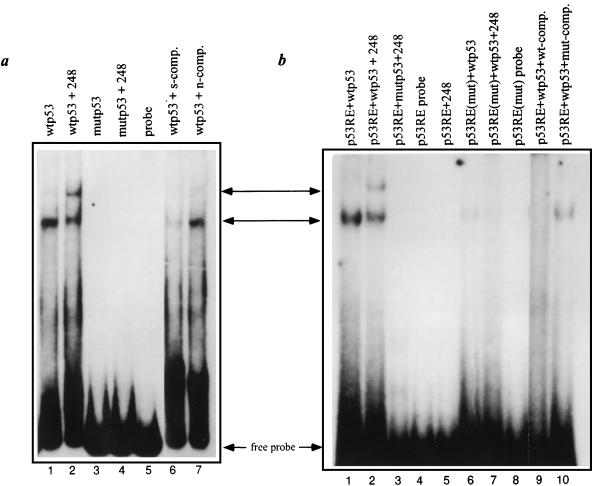
FIG. 5.
Binding of p53 to the c-fos p53-RE. (a) Equal amounts of a [32P]dATP end-labeled 180-bp probe prepared by PCR amplification (Fig. 3a) were incubated with 250 ng of either wt murine p53 (wtp53) or the murine p53cys270 mutant protein (mutp53), each purified from Sf9 cells infected with the corresponding recombinant baculovirus (53). Where indicated, reactions mixtures also included p53-specific monoclonal antibody PAb248 (lanes 2 and 4) or a 40× molar excess of a nonlabeled probe, which served as a specific competitor (s-comp., lane 6), or of the 180-bp multiple cloning site of pBluescript, which served as a nonspecific competitor (n-comp., lane 7). (b) Equal amounts of [32P]dATP end-labeled double-stranded 40-bp oligonucleotides [p53-RE and p53-RE(mut); Fig. 4b] were incubated with 250 ng of either wtp53 or p53cys270, with or without addition of PAb248 (lanes 2, 3, and 7; lane 5 contained PAb248 without p53). The reactions mixtures in lanes 9 and 10 also incubated a 150× molar excess of a nonlabeled 40-bp p53-RE oligonucleotide as a specific competitor (wt-comp., lane 9) or of p53-RE(mut) (lane 10). The arrows indicate the free probes and the shifted and supershifted bands.