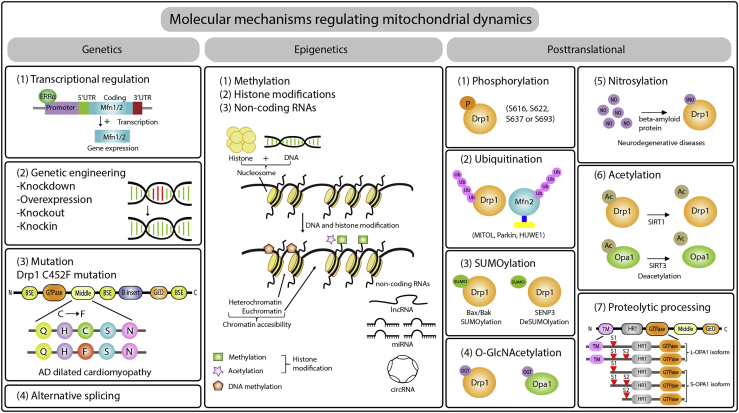
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of molecular mechanisms regulating mitochondrial dynamics
The left column indicates the mode of molecular dynamics regulation at the genomic level, which includes transcriptional regulation, genetic engineering, mutation, and alternative splicing. The second column demonstrates the epigenetic mechanisms of molecular dynamics regulation. The third column depicts the mechanism of molecular dynamics regulation at the posttranslational level. AD, autosomal dominant; P, phosphorylation; Ub, ubiquitin; SUMO, small ubiquitin-related modifier; OGT, O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) transferase; SNO, S-nitrosylation in serine residue; Ac, acetylation; S1 and S2, two proteolytic cleavage sites to generate a mix of long (L)- and short (S)-OPA1 isoforms. Opa1 possesses two proteolytic cleavage sites (S1 and S2), where their cleavage is mediated by two membrane-bound metalloproteases, OMA1 and YME1L, respectively.