Fig. 4.
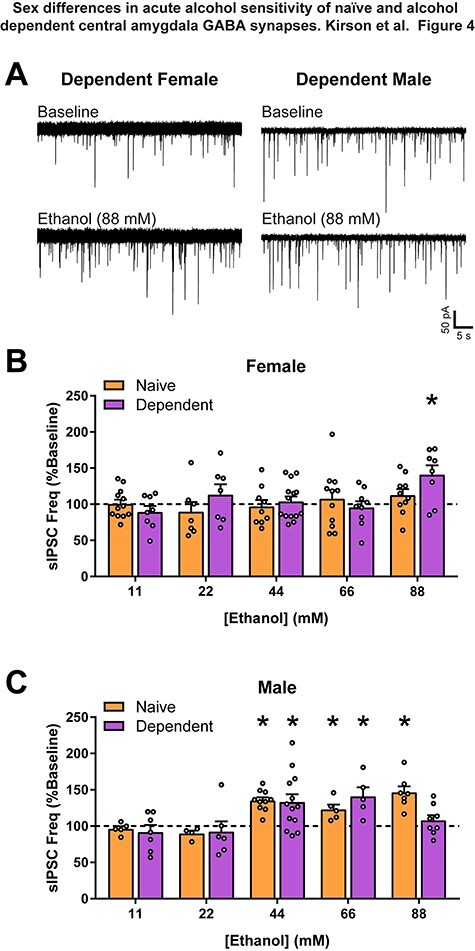
Alcohol dependent female CeA GABAergic transmission is only sensitive to high concentrations of alcohol. (A) Representative GABAA-mediated sIPSCs of CeA neurons from dependent female and male rats at baseline, and with subsequent acute application of a high concentration of alcohol (ethanol, 88 mM). (B) Acute alcohol at varying concentrations (ethanol; 11, 22, 44, 66 and 88 mM) has no effect on naïve female CeA sIPSC frequency. However, in dependent females, 88-mM alcohol increased sIPSC frequency (141 ± 12.74% of baseline). (C) Moderate acute alcohol concentrations increased CeA sIPSC frequency in both naïve (44: 135.3 ± 4.52% of baseline; 66: 122.9 ± 6.7% of baseline) and dependent (44: 133.2 ± 10.67% of baseline; 66: 141 ± 12.4% of baseline) males. However, 88-mM alcohol only increased sIPSC frequency in naïve males (150.9 ± 8.1% of baseline), with a lack of effect in dependent males (107.6 ± 7.3% of baseline). Lower concentrations of alcohol (11 and 22 mM) had no effect on sIPSC frequency in naïve or dependent males. n = 4–14 neurons per group. *Significant difference (P < 0.05).
