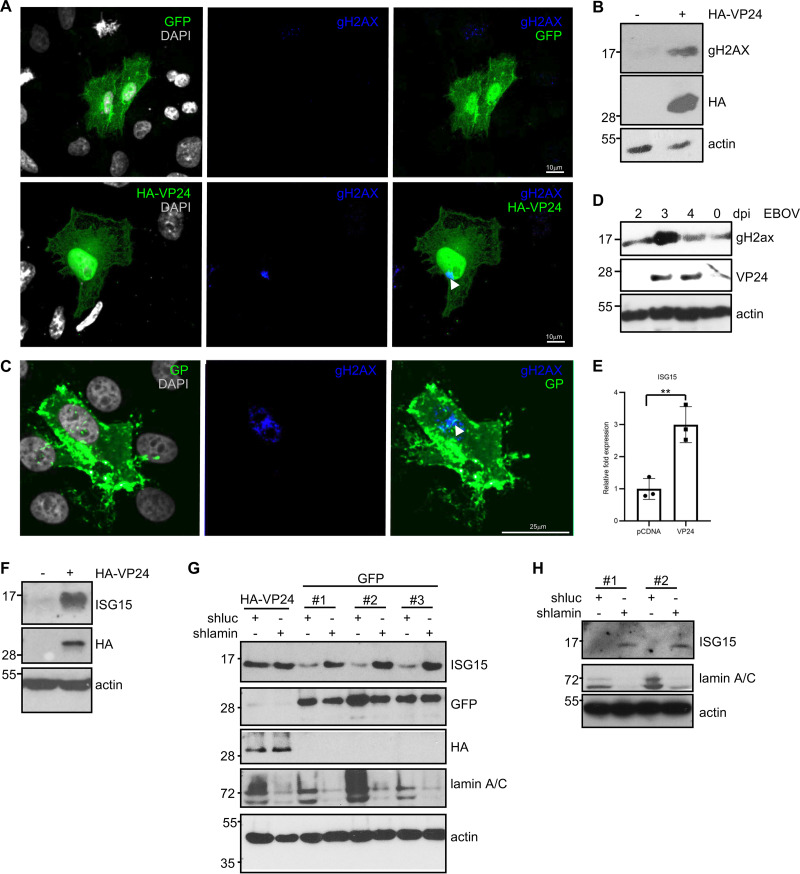
FIG 9.
Induction of DNA damage and upregulation of ISG15 by VP24. (A) Immunofluorescence staining using anti-gH2AX antibody of Vero cells transfected with 0.3 μg of HA-VP24. Arrowhead indicates positive detection of gH2AX in cells expressing VP24. (B) Western blotting using anti-gH2AX antibody in Vero cells transfected with 0.3 μg of HA-VP24. (C) Immunofluorescence staining using anti-gH2AX antibody in uninfected cells (EBOV GP negative) and in cells infected with EBOV (EBOV GP positive). (D) Western blotting using anti-VP24 and anti-gH2AX antibodies in HeLa cells at different times after infection with EBOV. The 0 time corresponds to mock-infected cells that were in culture for 4 days. (E) Transcriptional transactivation of ISG15 in response to VP24 expression by quantitative real-time PCR analysis. Columns are representative of the mean, and error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates. Statistical significance was assessed by a Student’s t test. **, P < 0.01. (F) A549 cells transfected with 0.3 μg of pcDNA or HA-VP24 plasmids were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-ISG15 antibody. (G) HeLa cells stably transfected with shluc or shlamin A plasmids were transfected as indicated and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-ISG15 antibody. Three replicates of HeLa cells transfected with shluc or shlamin are shown. (H) A549 cells stably transfected with shluc or shlamin A plasmids were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-ISG15 antibody. Two replicates are shown.