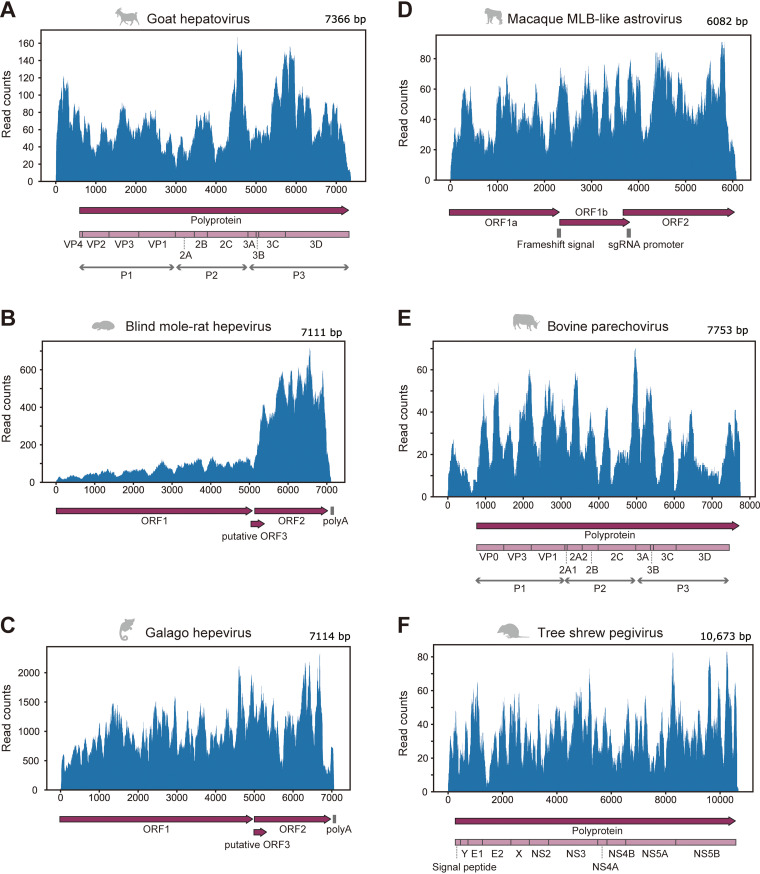
FIG 4.
Mapping analysis using RNA-seq data in which the full-length viral genome was identified. (A to F) Read distributions were mapped to the genomic sequence of goat hepatovirus (A), blind mole-rat hepevirus (B), galago hepevirus (C), macaque MLB-like astrovirus (D), bovine parechovirus (E), and tree shrew pegivirus (F). The upper panel shows the virus genomic positions (x axis) and read counts at each position (y axis). The lower panel shows genomic annotations, such as protein-coding regions or signal sequences. Dark purple arrows indicate open reading frames (ORFs) in the viral genome. Light purple boxes show mature proteins predicted based on aligned positions with reference viruses (see Materials and Methods). Gray vertical lines indicate nucleotide sequence features, such as polyadenylation signal [poly(A)], ribosomal frameshift signal (frameshift signal), and promoter sequence for subgenomic RNA synthesis (sgRNA promoter).