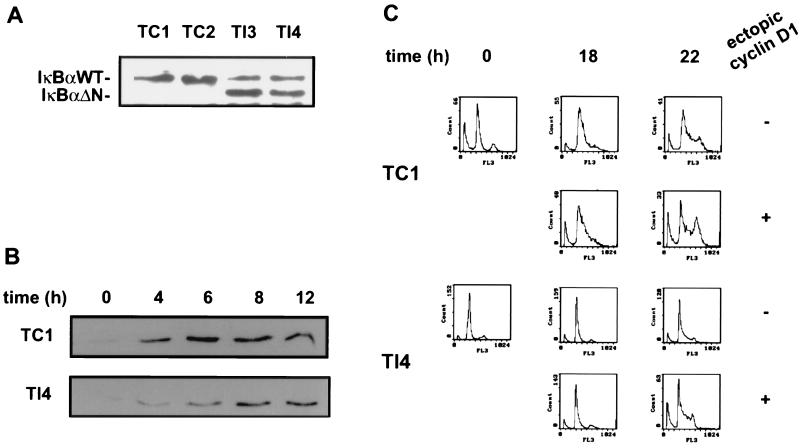
FIG. 7.
Retardation of G1-to-S-phase transition in T47DΔMTcycD1 cells, caused by NF-κB inactivation, was rescued by ectopic cyclin D1 expression. (A) Expression of IκBΔN in T47DΔMTcycD1 cells. Cells were transfected with an IκBΔN expression construct or an empty vector, and stable clones were selected with hygromycin (Sigma). Control and IκBΔN-transfected cells were lysed with extraction buffer and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-IκBα antibody. The positions of wild-type (WT) and mutant IκBα are indicated. Lanes 1 and 2, control clones (TC1 and TC2); lanes 3 and 4, IκBΔN-expressing clones (TI3 and TI4). (B) NF-κB-dependent cyclin D1 expression in T47DΔMTcycD1 cells. Western blots of protein extracts prepared from presynchronized TC1 and TI4 cells at the indicated time points after lovastatin removal and mevalonate addition are shown. Cyclin D1 was detected with the monoclonal antibody DCS-6. (C) FACS analysis of progression into S phase of TC1 and TI4 cells at 0, 18, or 22 h after lovastatin removal and mevalonate addition. Ectopic expression of cyclin D1 was induced by the addition of Zn2+ (+) or was not induced (−), as indicated. Progression through the cell cycle was monitored by detection of the DNA content. TC2 and TI3 cells (data not shown) gave similar results.