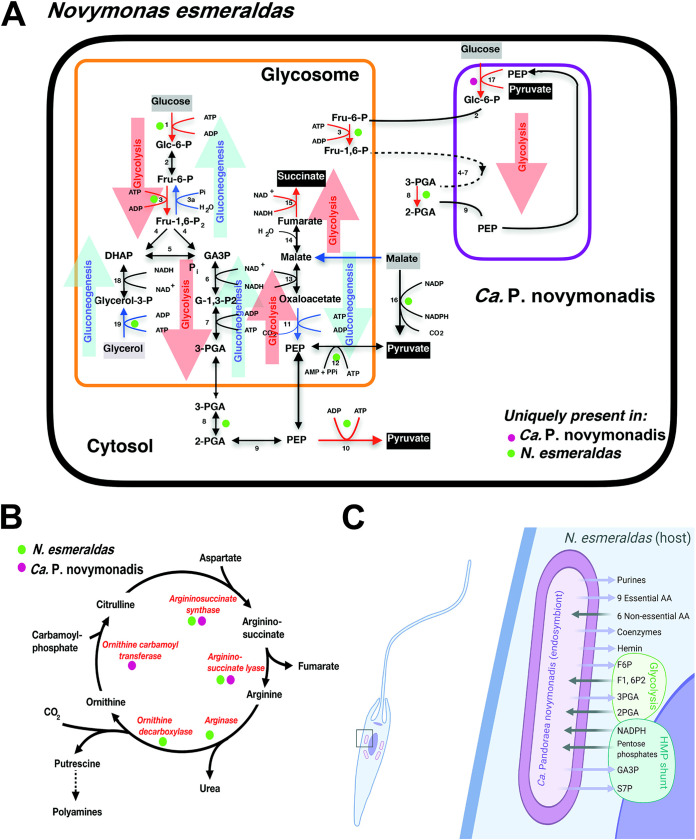
FIG 1.
Metabolic exchange between N. esmeraldas and its endosymbiont “Ca. Pandoraea novymonadis.” (A) Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. Boxed metabolites are nutrients (in gray) or end products (in black). Glycolysis (red arrows) takes place both in glycosomes and in the endosymbiont. In the latter, exchange of intermediates with the host organism occurs. Gluconeogenesis (blue arrows) takes place exclusively in the host, where malate (resulting from mitochondrial amino acid metabolism) and glycerol (formed from lipid hydrolysis) are converted to glucose 6-phosphate. Enzymes: 1, hexokinase; 2, phosphoglucose isomerase; 3, phosphofructokinase; 3a, fructose-bisphosphatase; 4, fructose-bisphosphate aldolase; 5, triosephosphate isomerase; 6, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; 7, phosphoglycerate kinase; 8, phosphoglycerate mutase; 9, enolase; 10, pyruvate kinase; 11, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; 12, pyruvate phosphate di-kinase; 13, malate dehydrogenase; 14, fumarate hydratase; 15, NADH-dependent fumarate reductase; 16, malic enzyme; 17, phosphoenolpyruvate-protein phosphotransferase. 18, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD); 19, glycerol kinase. Enzyme contributions by host and endosymbiont are indicated by dots of different colors. (B) The urea cycle of N. esmeraldas. The urea cycle is divided over host and endosymbiont. Enzyme contributions by host and endosymbiont are indicated by dots of different colors. (C) Summarized scheme of metabolic exchange between N. esmeraldas and its endosymbiont “Ca. Pandoraea novymonadis.” Abbreviations: F6P, fructose 6-phosphate; F1,6P2, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; 3PGA, 3-phosphoglycerate; 2PGA, 2-phosphoglycerate; S7P, sedoheptulose 7-phosphate; GA3P, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; HMP, hexose-monophosphate shunt, or pentose-phosphate pathway.