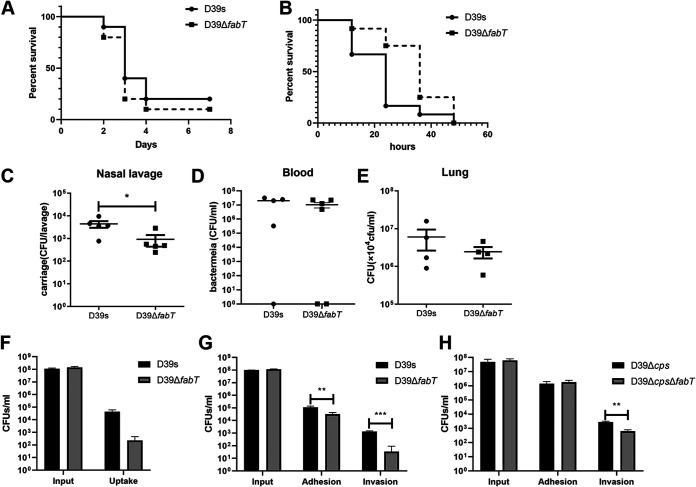
FIG 8.
In vivo and in vitro phenotypes of fabT mutant strains. (A) Survival experiments were performed by intranasal inoculation of 1 × 108 CFU S. pneumoniae into C57BL/6 mice. (B) Survival in the mouse septicemia model. Mice were injected intraperitoneally with 776 and 600 CFU of strains D39s and D39ΔfabT, respectively. (C to E) Intranasal infection with 1.5 × 107 CFU of S. pneumoniae. Bacterial loads were evaluated by cultures of (C) nasal lavage, (D) blood, and (E) lung homogenates. (F) Infection of mouse peritoneal primary macrophages with D39s and D39ΔfabT. MOI = 100:1. The input and the intracellular (uptake) bacteria were counted by plating from serial dilutions. (G and H) A549 epithelial cells were infected at an MOI of 100:1 with (G) D39s and (H) D39Δcps. Input, cell-associated (adhesion), and intracellular (invasion) bacteria were counted by plating from serial dilutions.