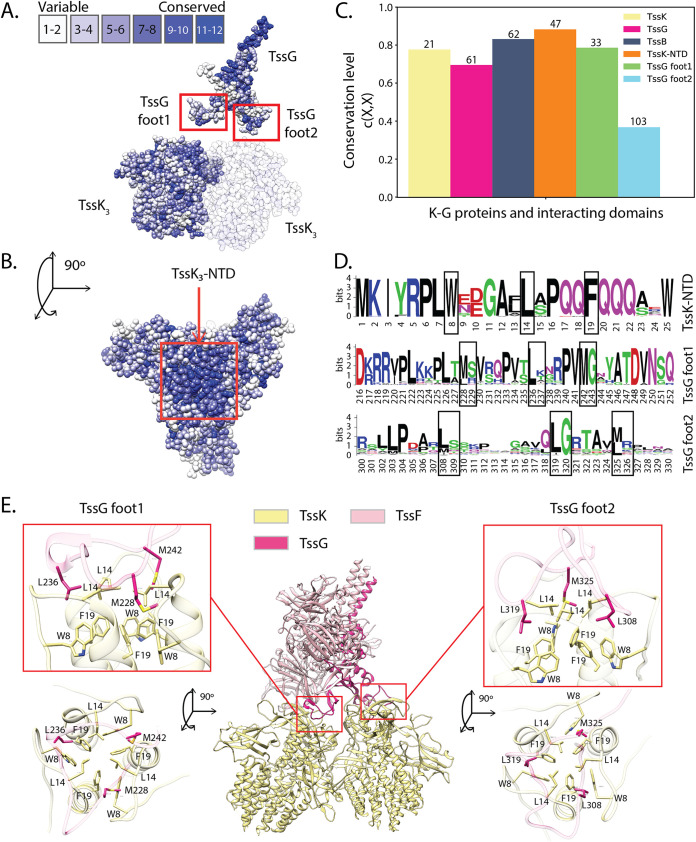
FIG 2.
EAEC TssK-TssG interface conservation. (A and B) TssK and TssG residue conservation obtained with aligned EAEC variants mapped on the EAEC wedge complex structure (PDB 6N38). A dense group of highly conserved residues can be observed on the top of TssK trimers. This is particularly visible in panel B, in the top view of the trimer. TssG exhibits another group of conserved residues on its antenna (A), which is the domain involved in the interaction with the two TssF copies of the wedge complex. (C) Conservation level for TssK, TssK NTD, TssG, TssG foot 1, TssG foot 2, and TssB on EAEC. The numbers at the top of the bars indicate the amount of aligned EAEC homolog sequences used to compute the conservation level. (D) Sequence logos illustrating the residue conservation of the TssK-TssG interacting regions for EAEC close homologs. The height of each letter represents the information content of the corresponding amino acid at that position in bits. Black boxes highlight the three hydrophobic residues forming the TssK NTD hydrophobic cavity on top of TssK trimers and the TssG foot LG repeats. (E) TssK-TssG binding sites. The triangular TssG loops, foot 1 and foot 2, bind TssK trimers on its N-terminal region. These contacts are mediated by hydrophobic interactions between the TssK NTD hydrophobic cavity and the conserved LG repeats of both feet.