FIG 3.
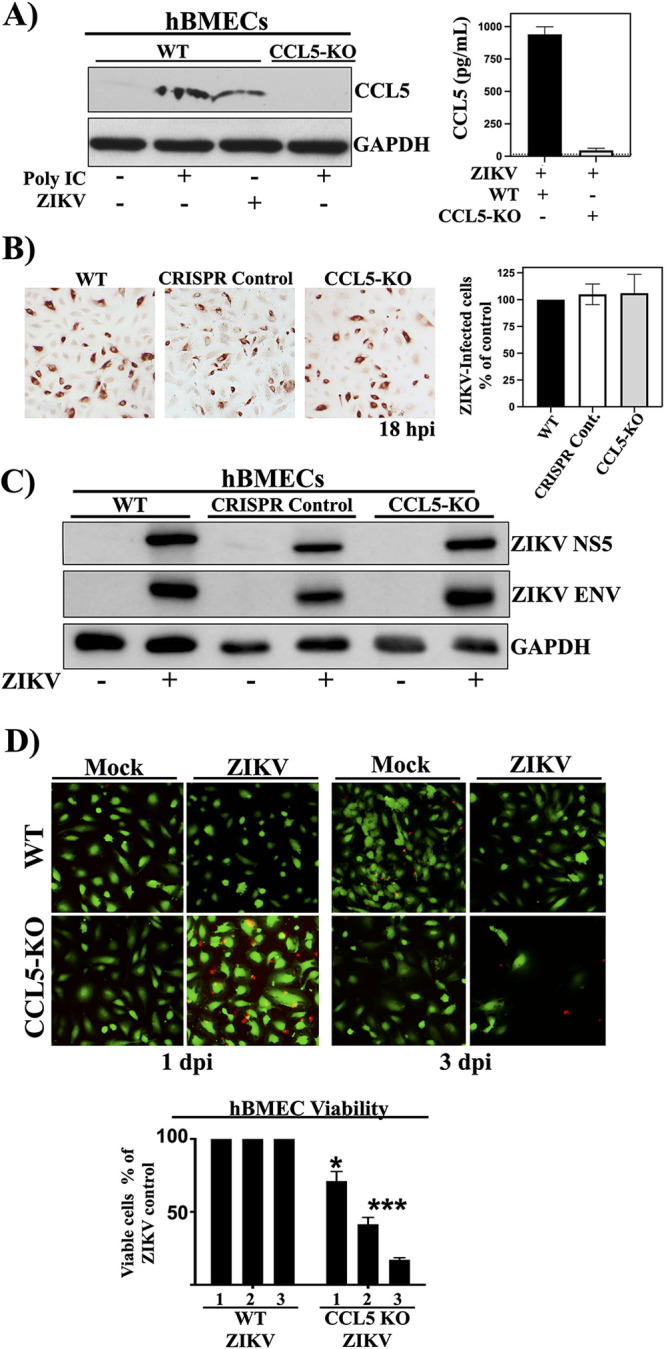
CCL5-KO reduces hBMEC viability during ZIKV infection. (A) WT and puromycin-selected CCL5-KO hBMECs were transfected with poly(I/C) (0.5 μg/ml) or ZIKV infected (MOI of 10) and evaluated for CCL5 expression by Western blotting and an ELISA (24 h posttransfection). (B and C) WT, CRISPR control, and CCL5-KO hBMECs were ZIKV infected (MOI of 10), and at 18 hpi, comparable ZIKV infections were detected by ZIKV antigen-positive cells (B) and Western blot detection of ZIKV NS5 and ZIKV Env, compared with GAPDH controls (C). (D) hBMECs were costained with calcein-AM (live)/propidium iodide (dead), and the viability of hBMECs was quantified by CyQuant analysis at 1 to 3 dpi compared to mock-infected WT hBMECs. Experiments were performed at least 3 times with similar results.
