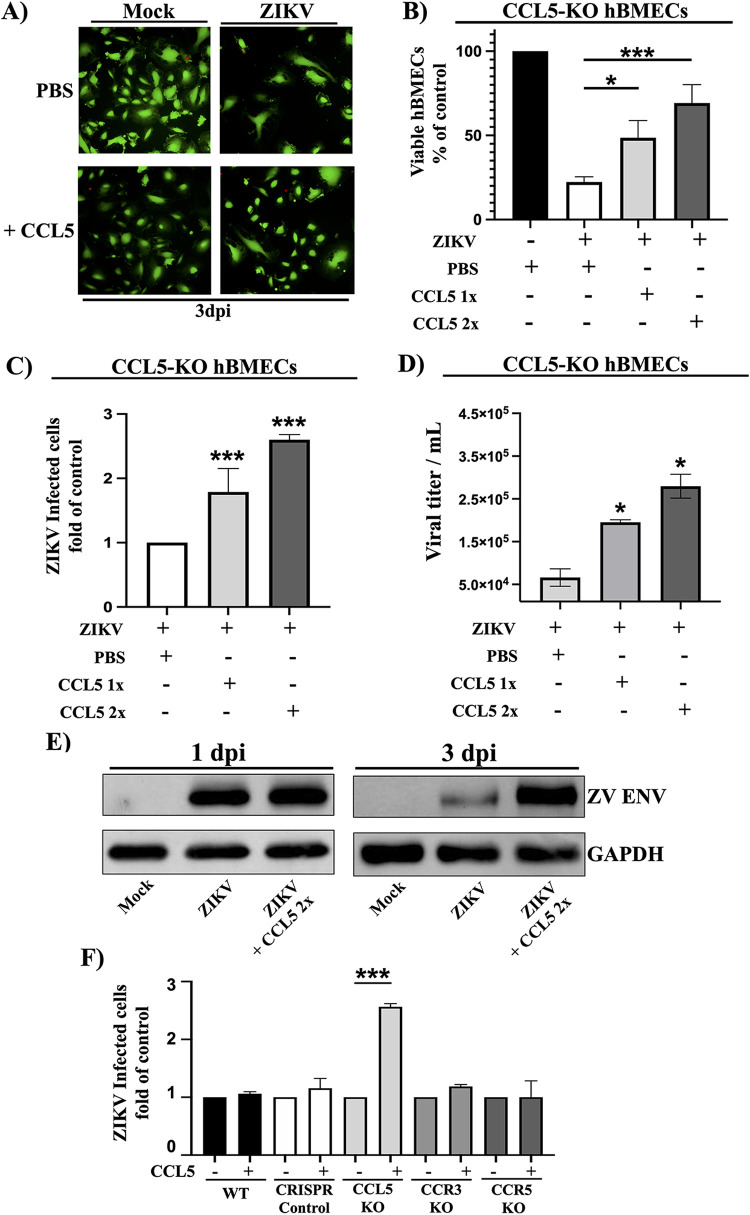
FIG 5.
Exogenous CCL5 rescues the viability and persistence of ZIKV-infected CCL5-KO hBMECs. (A to D) CCL5-KO hBMECs were mock or ZIKV infected (MOI of 10) and control treated with PBS or CCL5 (100 ng/ml) once daily or twice daily to 3 dpi. At 3 dpi, CCL5-KO hBMECs were assessed for viability via calcein-AM/propidium iodide staining (A) and quantified by CyQuant analysis (B) for ZIKV-infected hBMECs (C) and viral titers (D). (E) Lysates of CCL5-KO hBMECs treated with PBS or CCL5 twice daily for 1 and 3 dpi were assessed for ZIKV (ZV) Env, compared to GAPDH controls. (F) WT, CRISPR control, CCL5-KO, CCR3-KO, and CCR5-KO hBMECs were ZIKV infected as described above; control treated with PBS or CCL5 (100 ng/ml) twice a day for 3 dpi; and assessed for ZIKV infection. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001). Experiments were performed at least 3 times with similar results.