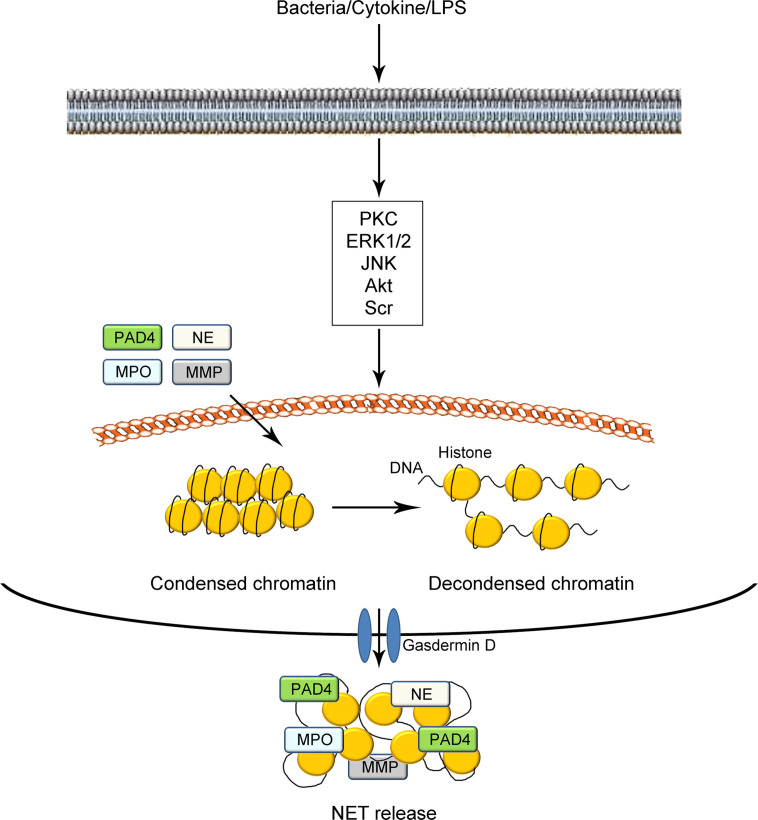
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of NET formation. Under certain stimuli such as bacterial infection, cytokines, and LPS challenge, neutrophils are activated via the modulation of cellular signaling pathways mediated by PKC, EK1/2, JNK, Akt, Scr, and so on. The tight electrostatic binding between DNA strands and histones in nucleosomes is weakened, mediated by two kinds of proteases including PAD4 and NE. The decondensed DNA with citrullinated histones catalyzed by PAD4 are decorated with several granule proteins including PAD4, NE, MPO, MMP, and gasdermin D and expelled from neutrophils as NETs. NETs, neutrophil extracellular traps; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PKC, protein kinase C; ERK1/2, extracellular regulated protein kinase 1/2; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; PAD4, peptidyl arginine deiminase 4; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NE, neutrophil elastase; MPO, myeloperoxidase.